3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(10):1363-1376. doi:10.7150/ijms.85746 This issue Cite
Review
Repeated Low-Level Red-Light Therapy for Controlling Onset and Progression of Myopia-a Review
1. Department of Pediatric Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University, Kunming 650021, China.
2. Department of Ophthalmology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650031, China.
3. BioTissue (Tissue Tech, Inc.), Ocular Surface Center, and Ocular Surface Research & Education Foundation, Miami, FL, 33126 USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
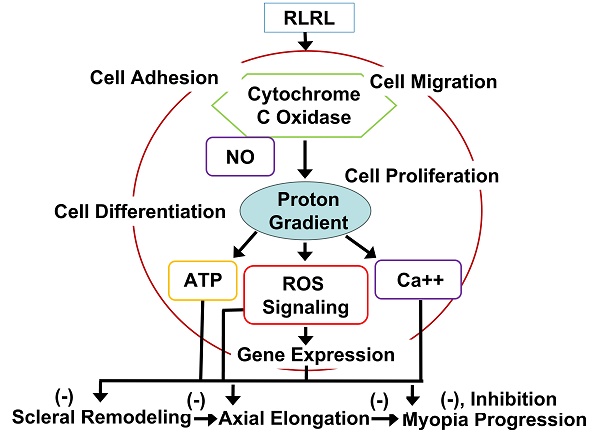
Repeated low-level red-light (RLRL), characterized by increased energy supply and cellular metabolism, thus enhancing metabolic repair processes, has gained persistent worldwide attention in recent years as a new novel scientific approach for therapeutic application in myopia. This therapeutic revolution led by RLRL therapy is due to significant advances in bioenergetics and photobiology, for instance, enormous progresses in photobiomodulation regulated by cytochrome c oxidase, the primary photoreceptor of the light in the red to near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, as the primary mechanism of action in RLRL therapy. This oxidase is also a key mitochondrial enzyme for cellular bioenergetics, especially for the nerve cells in the retina and brain. In addition, dopamine (DA)-enhanced release of nitric oxide may also be involved in controlling myopia by activation of nitric oxide synthase, enhancing cGMP signaling. Recent evidence has also suggested that RLRL may inhibit myopia progression by inhibiting spherical equivalent refraction (SER) progression and axial elongation without adverse effects.
In this review, we provide scientific evidence for RLRL therapy as a unique paradigm to control myopia and support the theory that targeting neuronal energy metabolism may constitute a major target for the neurotherapeutics of myopia, with emphasis on its molecular, cellular, and nervous tissue levels, and the potential benefits of RLRL therapy for myopia.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact