3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1888-1902. doi:10.7150/ijms.76660 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Bioinformatics Perspective on the Dysregulation of Ferroptosis and Ferroptosis-related Immune Cell Infiltration in Alzheimer's Disease
1. Department of Ophthalmology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
2. Department of Neurology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Abstract
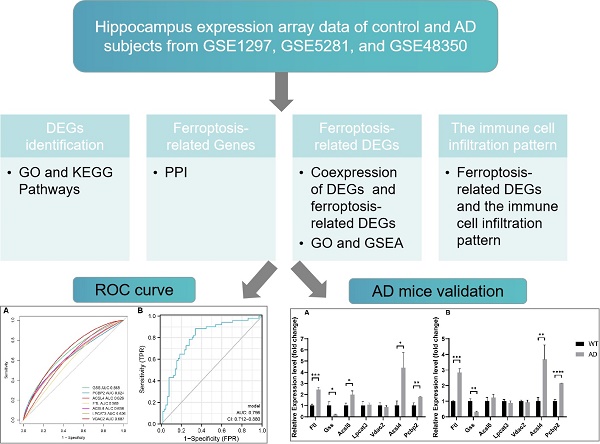
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent dementia worldwide, but its pathophysiology and molecular events remain unknown. Herein, we first analyzed the differential expression pattern of patients' AD hippocampus through gene expression array data from the GEO database. Notch2nl, TGFB1I1, and LTF were up-regulated in AD patients, while ARPC1A, CHGB, and MPV17 down-regulated. Second, dysregulation of ferroptosis related genes was demonstrated from our data: PCBP2 and FTL significantly up-significant in AD hippocampus, while VDAC2, LPCAT3, GSS, ACSL4, and ACSL6 significantly down-regulated. The protein-protein interactions (PPI) network revealed that FTL was involved in iron metabolism and utilization, while ACSL4 and ACSL6 were involved in a polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolism network. Gene correlation analysis on differential expressed genes (DEGs) indicated that ferroptosis regulates a series of biological processes and pathways related to AD pathogenesis. Third, ferroptosis-related DEGs regulated the immune cell infiltration pattern in the AD hippocampus, characterized by decreased memory B cells, increased memory resting CD4+ T cells, memory activated CD4+ T cells, and resting NK cells. The altered expression of ferroptosis-related DEGs affected the infiltration of specific immune cell types. The model constructed by the seven ferroptosis-related differential genes may accurately predict the outcome of AD occurrence. Finally, qPCR validation on these ferroptosis-related DEGs in APPswe/PSEN1dE9 mice confirmed the dysregulated expression of Pcbp2, FTL, GSS, and ACSL4 in the AD hippocampus and forebrain. In conclusion, our results supported the conception that the AD brain revealed dysregulated ferroptosis and immune cell infiltration.
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease, ferroptosis, immune cell infiltration, hippocampus

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact