3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):2842-2848. doi:10.7150/ijms.61891 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Effects of renal impairment on cardiac remodeling and clinical outcomes after myocardial infarction
1. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan.
2. Department of Optometry, Chung Hwa University of Medical Technology, Rende District, Tainan.
3. Department of Health and Nutrition, Chia Nan University of Pharmacy and Science, Tainan.
4. Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan.
5. Department of Pharmacy, Chia Nan University of Pharmacy and Science, Tainan.
6. Department of Hospital and Health Care Administration, Chi-Mei Medical Center, Tainan.
7. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan.
8. Department of Biotechnology, Southern Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Tainan.
9. Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan.
Abstract
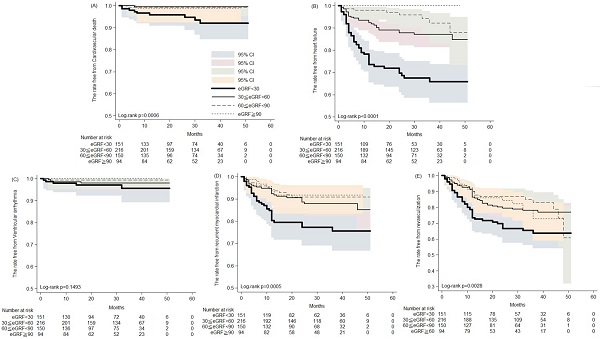
How renal function influences post-acute myocardial infarction (AMI) cardiac remodeling and outcomes remains unclear. This study evaluated the impact of levels of renal impairment on drug therapy, echocardiographic parameters, and outcomes in patients with AMI undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). A total of 611 patients diagnosed with AMI underwent successful PCI, and two echocardiographic examinations were performed within 1 year after AMI. Patients were categorized according to Group 1: severely impaired estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)<30, Group 2: mildly impaired 30≤eGFR<60, Group 3: potentially at risk 60≤eGFR<90 and normal eGFR≥90 ml/min/1.73 m2. During the 5-year follow-up period, the primary endpoints were cardiovascular mortality and outcomes. Patients with worse renal function (eGFR<30) were older and had a higher prevalence of hypertension and diabetes, but relatively few were smokers or had hyperlipidemia. Despite more patients with lesions of the left anterior descending artery, those with worse renal function received suboptimal guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). Notably, patients with worse renal function presented with worse left ventricular function at baseline and subsequent follow-up. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed increased cardiovascular death, development of heart failure, recurrent AMI and revascularization in patients with worse renal function. Notably, as focusing on patients with ST elevation MI, the similar findings were observed. In multivariable Cox regression, impaired renal function showed the most significant hazard ratio in cardiovascular death. Collectively, in AMI patients receiving PCI, outcome differences are renal function dependent. We found that patients with worse renal function received less GDMT and presented with worse cardiovascular outcomes. These patients require more attention.
Keywords: post myocardial infarction, cardiac remodeling, renal function, mortality, heart failure

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact