3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1312-1317. doi:10.7150/ijms.55017 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Comparison of abdominal and minimally invasive radical hysterectomy in patients with early stage cervical cancer
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Vincent's hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Seoul St. Mary's hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to compare survival outcomes of open radical hysterectomy and minimally invasive radical hysterectomy (MIS) in early stage cervical cancer.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 148 patients with stage IB1 - IIA2 cervical cancer who underwent either minimally invasive or open radical hysterectomy. Tumor characteristics, recurrence rate, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS) were compared according to surgical approach.
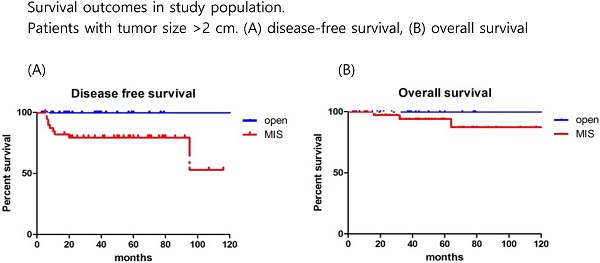
Results: In total, 110 and 38 patients were assigned to open surgery and MIS groups. After a medical follow-up of 42.1 months, the groups showed similar survival outcomes (recurrence rate, DFS, and OS). However, in patients with tumor size >2 cm, recurrence rate was significantly higher in MIS group (22.5% vs 0%; p=0.008). And in patients with tumor size >2 cm, MIS group showed significantly poorer DFS than open surgery group (p=0.017), although OS was similar between the two groups (p=0.252).
Conclusion: In patients with tumor size >2 cm, MIS was associated with higher recurrence rates and poorer DFS than open surgery. However, in patients with tumor size ≤2 cm, MIS did not seem to compromise oncologic outcomes.
Keywords: cervical cancer, minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic surgery, radical hysterectomy, LACC trial

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact