ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(6):1064-1071. doi:10.7150/ijms.90341 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association of IL-18 gene polymorphisms with clinical aspects of hyperlipidemia in middle-aged and early people in the community
1. School of Life Science, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan.
2. Translational medicine center, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei City, Taiwan.
3. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
4. Department of Neurology, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei 111045, Taiwan.
5. School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
6. Department of Neurology, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
7. Institute of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei 100025, Taiwan.
8. School of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan 33302, Taiwan.
9. Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung 204201, Taiwan.
10. Department of Respiratory Therapy, Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
11. Department of Public Health, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
12. School of Public Health, College of Public Health, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Abstract
Hyperlipidemia is notorious for causing coronary artery disease (CAD). IL-18 is a proinflammtory cytokine that contributes to the pathogenesis of CAD. Previous reports have revealed that genetic polymorphism of IL-18 is associated with its expression level as well as the susceptibility to CAD. In the present study, we aim to investigate the relationship between IL-18 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and hyperlipidemia in the Han Chinese population in Taiwan. A total of 580 participants older than 30 were recruited from the community. We collected the demographics, self-reported disease histories, and lifestyles. We also assessed the levels of lipid profiles including total cholesterol (CHOL), triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Two SNPs, rs3882891C/A (intron 5) and rs1946518A/C (promoter -607) of IL-18 were elucidated by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) methods. Our results revealed that rs3882891 AA was associated with lower risk of hypercholesterolemia, higher CHOL and LDL-C in subjects (p=0.003, p=0.000 and p=0.005 separately), and rs1946518 CC was associated with hypercholesterolemia, higher CHOL and LDL-C as well (p=0.021, p=0.003 and p=0.001 separately)
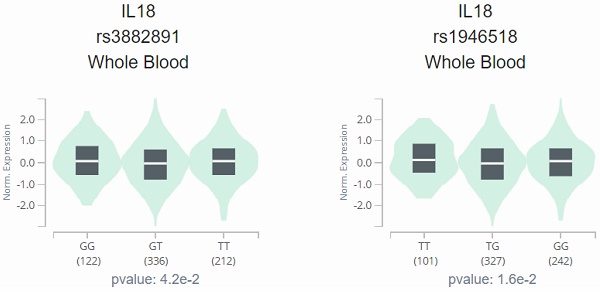
Furthermore, both SNPs were associated with IL-18 expression level, which was examined by Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal (p=0.042 and 0.016 separately). Finally, the haplotype of IL-18 was subsequently arranged in the order of rs3882891 and rs1946518. The result revealed that the AC haplotype of 2 IL-18 SNPs was also associated with lower risk of hypercholesterolemia, lower levels of CHOL and LDL-C (p=0.01, p=0.001 and 0.003). The current study is the first to report the association between IL-18 SNPs and hyperlipidemia in the Chinese Han population.
