3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):151-168. doi:10.7150/ijms.86591 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bibliometric Analysis of Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke (2001-2022): Trends, Hotspots and Prospects
1. Department of Neurology, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Taiyuan, 030000, China.
2. Shanxi Cardiovascular Hospital, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030000, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Cellular Physiology, of Ministry of Education, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030000, China.
4. Department of Neuroscience, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, 999077, China.
5. The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Research Centre of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong, 030600, China.
6. Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases, Medical School of Shanxi Datong University, Datong, 037000, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
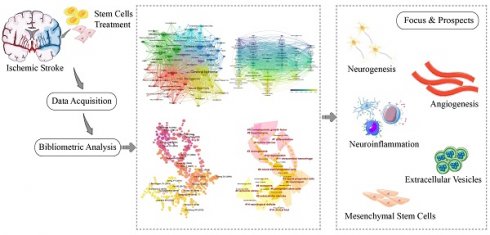
Background: Ischemic stroke is a common cerebrovascular accident with a high risk of neurological deficits. Stem cell therapy has progressively attracted the interest of scientists and clinicians due to the benefits of promoting neural regeneration and regulating the microenvironment surrounding the lesion after ischemic stroke. Our study aimed to evaluate the development trends and research hotspots in the field of stem cells and ischemic stroke.
Materials and methods: Publications related to stem cells and ischemic stroke were retrieved from the Web of Science from 2001 to 2022. Data analysis and mapping were performed using VOSviewer, Citespace and ImageGP.
Results: In total, 1932 papers were included in the analysis. Publications have steadily increased over the past 22 years. China has contributed the maximum number of publications, whereas the USA ranked first in the total number of citations and was considered the center of the international collaboration network. University of South Florida, Henry Ford Hospital, and Oakland University were the most influential institutions. Stroke, Brain Research, and Neural Regeneration Research were the most productive journals. The research in this field was primarily focused on the effects of stem cells on neurogenesis, inflammation, and angiogenesis following ischemic stroke, as well as their therapeutic potential for the disease. In addition, neural stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells are the most commonly utilized stem cells. The topics related to miRNA, extracellular vesicles, exosomes, mesenchymal stem cells, neuroinflammation, and autophagy are current research hotspots.
Conclusion: Our bibliometric study provides a novel perspective on the research trends in the field of stem cells and ischemic stroke. The outcome of this study may benefit scientists to identify research hotspots and development directions, thereby advancing the application of stem cell-based therapy for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke, Stem cells, Bibliometric analysis, Neurogenesis, Paracrine effects, Translation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact