Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):107-122. doi:10.7150/ijms.88748 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid-Induced Acute Pulmonary Inflammation and NF-κB Activation in Mice by a Banana Plant Extract
1. Cancer Center, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11696, Taiwan.
2. Department of Chinese Medicine, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien 97002, Taiwan.
3. Traditional Chinese Medicine Cancer Center, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Hualien 97002, Taiwan.
4. Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei, 11529, Taiwan.
5. Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11696, Taiwan.
6. Chimera Bioscience Inc., No. 18 Siyuan St., Zhongzheng Dist., Taipei 10087, Taiwan.
7. Department of Research and Development, Natural Well Technical Company, Guishan, Taoyuan 33377, Taiwan.
8. Department of Medical Education and Research, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11696, Taiwan.
9. Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
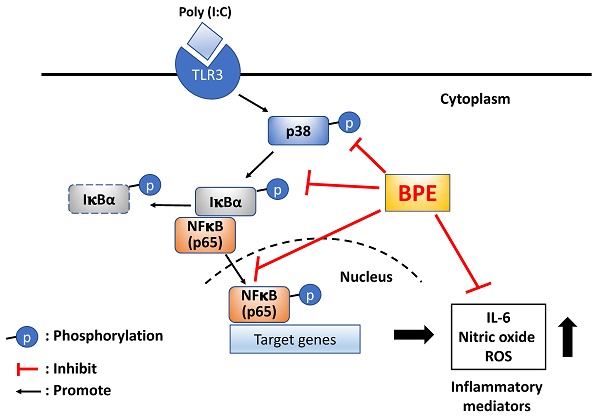
NF-κB activation is pivotal for the excess inflammation causing the critical condition and mortality of respiratory viral infection patients. This study was aimed to evaluate the effect of a banana plant extract (BPE) on suppressing NF-κB activity and acute lung inflammatory responses in mice induced by a synthetic double-stranded RNA viral mimetic, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly (I:C)). The inflammatory responses were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and HE stains and ELISA. The NF-κB activities were detected by immunohistochemistry in vivo and immunofluorescence and Western blot in vitro. Results showed that BPE significantly decreased influx of immune cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes, and total WBC), markedly suppressed the elevation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (IL-6, RANTES, IFN-γ, MCP-1, keratinocyte-derived chemokine, and IL-17), and restored the diminished anti-inflammatory IL-10 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of poly (I:C)-stimulated mice. Accordingly, HE staining revealed that BPE treatment alleviated poly (I:C)-induced inflammatory cell infiltration and histopathologic changes in mice lungs. Moreover, immunohistochemical analysis showed that BPE reduced the pulmonary IL-6, CD11b (macrophage marker), and nuclear NF-κB p65 staining intensities, whilst restored that of IL-10 in poly (I:C)-stimulated mice. In vitro, BPE antagonized poly(I:C)-induced elevation of IL-6, nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, NF-κB p65 signaling, and transient activation of p38 MAPK in human lung epithelial-like A549 cells. Taken together, BPE ameliorated viral mimic poly(I:C)-induced acute pulmonary inflammation in mice, evidenced by reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and regulation of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. The mechanism of action might closely associate with NF-κB signaling inhibition.
Keywords: banana plant extract, acute pulmonary inflammation, IL-6, NF-κB

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact