3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):19-26. doi:10.7150/ijms.88147 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Assessment of renal quality with quantitative contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for differentiating kidney histopathology before procurement
1. Institute of Organ Transplantation, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology; Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Ministry of Education; NHC Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation; Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Wuhan, China.
2. Department of Medical Ultrasound, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
#Shangxin Dong and Bo Zhang contributed equally to this work.
*Hongchang Luo and Jipin Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
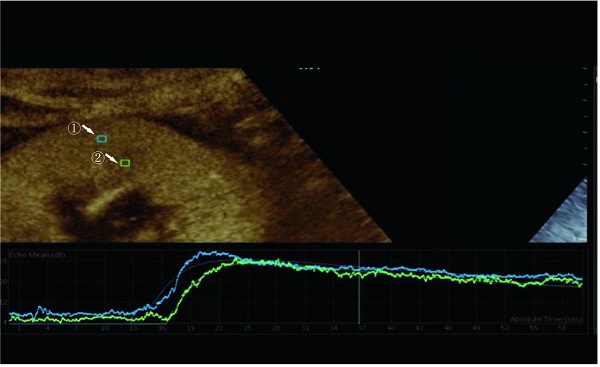
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the use of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) to assess the kidneys' quality before procurement.
Methods: This prospective study included 74 donors and 148 recipients of kidneys. 119 kidneys underwent quantitative analysis. Before organ procurement, potential kidney donors underwent CEUS, though organ procurement involved a zero-point puncture biopsy. CEUS parameters of the renal cortex and medulla were evaluated, including rise time (RT), time to peak (TTP), the area under the curve (AUC), wash-in slope (WIS), peak intensity (PI), and mean transit time (MTT). Donors' kidneys were classified based on their pathological. Additionally, short-term clinical indicators of renal recipients were collected and analyzed to determine whether the patients had delayed recovery of renal allograft function.
Results: This experiment included 148 cases of kidney information, divided into two groups based on the Remuzzi score of the kidneys. However, 29 kidneys were excluded from the quantitative analysis due to loss or low quality of CEUS images. Comparing the time-intensity curve (TIC) of renal cortical region of interest (ROI), we found that the group with lower pathological scores exhibited higher PI (P=0.002), AUC(P=0.003), and WIS (P=0.009). TIC comparison results for renal medulla ROI revealed that the group with lower pathological scores had higher PI (P=0.010), AUC (P=0.023), and WIS (P=0.024).
Conclusions: This study highlighted the potential of CEUS as a non-invasive, safe, and real-time examination method that correlates with the Remuzzi score and renal pathology. Therefore, it can be used as a prospective preoperative non-invasive evaluation method for the donor's kidney.
Keywords: contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, kidney transplantation, organ procurement, donor selection

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact