3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):8-18. doi:10.7150/ijms.84154 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Quantitative DNA Methylation Analysis and Epigenotype-Phenotype Correlations in Taiwanese Patients with Silver-Russell Syndrome
1. Department of Medicine, MacKay Medical College, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
2. Department of Pediatrics, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
3. Department of Medical Research, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
4. MacKay Junior College of Medicine, Nursing and Management, Taipei, Taiwan.
5. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Rare Disease Center, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
7. Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
8. Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang-Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan.
9. Department of Pediatrics, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
10. Department of Pediatrics, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu, Taiwan.
11. Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
12. Department of Pediatrics, National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan.
13. Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Medical University Chung Ho Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
14. Department of Pediatrics, Changhua Christian Children's Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan.
15. Department of Pediatrics, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
16. Department of Pediatrics, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
17. Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
18. Department of Pediatrics, China Medical University Hsinchu Hospital, Taiwan.
19. College of Medicine, Fu-Jen Catholic University, Taipei, Taiwan.
20. Department of Infant and Child Care, National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Sciences, Taipei, Taiwan.
Abstract
Background: Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS; OMIM #180860) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous imprinting disorder characterized by prenatal and postnatal growth failure. The aim of this study was to identify the epigenotype-phenotype correlations in these patients using quantitative DNA methylation analysis.
Methods: One hundred and eighty-three subjects clinically suspected of having SRS were referred for diagnostic testing by the methylation profiling of H19-associated imprinting center (IC) 1 and imprinted PEG1/MEST regions using methylation-specific high-resolution melting analysis and methylation quantification with the MassARRAY assay. Correlations between quantitative DNA methylation status and clinical manifestations of the subjects according to the Netchine-Harbison (N-H) clinical scoring system for SRS were analyzed.
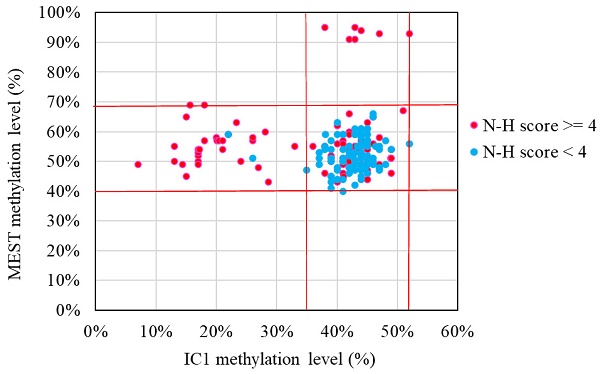
Results: Among the 183 subjects, 90 had a clinical diagnosis of SRS [N-H score ≥ 4 (maximum = 6)] and 93 had an SRS score < 4. Molecular lesions were detected in 41% (37/90) of the subjects with a clinical diagnosis of SRS, compared with 3% (3/93) of those with an N-H score < 4. The IC1 methylation level was negatively correlated with the N-H score. The molecular diagnosis rate was positively correlated with the N-H score. Thirty-one subjects had IC1 hypomethylation (IC1 methylation level <35% by the MassARRAY assay), seven had maternal uniparental disomy 7, and two had pathogenic copy number variants. Among the 90 subjects with an N-H score ≥ 4, the IC1 methylation level was significantly different between those with or without some clinical SRS features, including birth length ≤ 10th centile, relative macrocephaly at birth, normal cognitive development, body asymmetry, clinodactyly of the fifth finger, and genital abnormalities.
Conclusions: This study confirmed the suitability of the N-H clinical scoring system as clinical diagnostic criteria for SRS. Quantitative DNA methylation analysis using the MassARRAY assay can improve the detection of epigenotype‐phenotype correlations, further promoting better genetic counseling and multidisciplinary management for these patients.
Keywords: epigenotype, MassARRAY, Netchine-Harbison clinical scoring system, phenotype, quantitative DNA methylation, Silver-Russell syndrome

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact