ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(8):1046-1059. doi:10.7150/ijms.84940 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel prognostic signature of chemokines for survival and immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
Department of Pathology, ZhangZhou Affiliated Hospital of FuJian Medical University, Zhangzhou city, Fujian Province 363000, China
Abstract
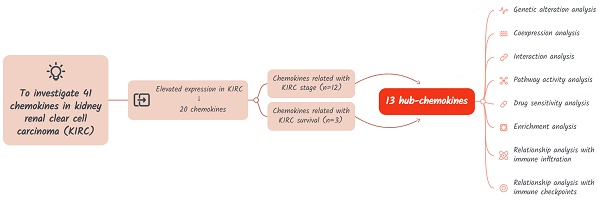
Objective: Studies have revealed the alteration of chemokines in the tumour microenvironment in renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), which is closely related with immune infiltration and the prognosis of patients with KIRC. This research aims to comprehensively clarify the signature of chemokines in KIRC and the correlation between chemokines and immune infiltration in the TME of KIRC.
Methods: The chemokine expression in KIRC were investigated by using multiple multiomics and bioinformatics tools. Hub-chemokines that were significantly related with the cancer stage and survival were identified. The role of hub-chemokines in the tumor microenvironment of KIRC was further assessed by using enrichment analysis, cancer-related pathway and immune infiltration analysis.
Results: A total of 20 chemokines were significantly elevated in KIRC. Based on the correlation with KIRC stages and survival, 13 hub-chemokines were identified. Among the hub-chemokines, the high expression of CXCL2, CXCL5 and CXCL13 were related with worse survival of KIRC patients. The hub-chemokines were associated with the activation of multiple cancer-related signaling pathways. The functions of hub-chemokines were mainly enriched in chemokine-mediated signaling pathway, immunocytes chemotaxis and chemokine activity. CCL4, CCL5, CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 were related with various types immune infiltration such as CD8+T cell, neutrophil, B cell and dendritic cell. Using the hub-chemokine CXCL10, multiple immune checkpoints including LAG3, CTLA-4 and PD-1 were identified.
Conclusion: Our research sheds light on the chemokines and their important role in promoting the tumor microenvironment of KIRC. The findings could provide more data about the prognosis prediction and treatment targets for KIRC.
Keywords: kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, chemokine, tumour microenvironment, immune infiltration, immune checkpoint

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact