3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):969-975. doi:10.7150/ijms.84364 This issue Cite
Research Paper
WWOX Polymorphisms as Predictors of the Biochemical Recurrence of Localized Prostate Cancer after Radical Prostatectomy
1. Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
2. School of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
3. School of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan.
4. Institute of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
5. Department of Family Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chi Nan University, Nantou, Taiwan.
7. Department of Medicine and Nursing, Hungkuang University, Taichung, Taiwan.
8. Department of Urology, Tung's Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
9. Department of Medical Research, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
Abstract
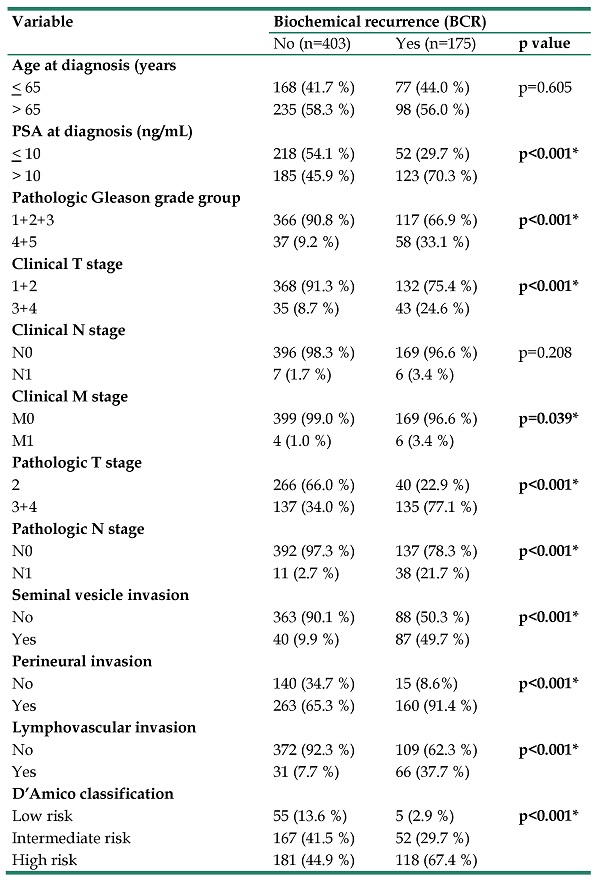
The downregulation of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX), a tumor suppressor gene, is associated with the tumorigenesis and poor prognosis of various cancers. In this study, we investigated the associations between the polymorphisms of WWOX, clinicopathologic features of prostate cancer (PCa), and risk of postoperative biochemical recurrence (BCR). We evaluated the effects of five single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of WWOX on the clinicopathologic features of 578 patients with PCa. The risk of postoperative BCR was 2.053-fold higher in patients carrying at least one “A” allele in WWOX rs12918952 than in those with homozygous G/G. Furthermore, patients with at least one polymorphic “T” allele in WWOX rs11545028 had an elevated (1.504-fold) risk of PCa with seminal vesicle invasion. In patients with postoperative BCR, the risks of an advanced Gleason grade and clinical metastasis were 3.317- and 5.259-fold higher in patients carrying at least one “G” allele in WWOX rs3764340 than in other patients. Our findings indicate the WWOX SNPs are significantly associated with highly aggressive pathologic features of PCa and an elevated risk of post-RP biochemical recurrence.
Keywords: WWOX, prostate cancer, polymorphism, biochemical recurrence

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact