3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):870-887. doi:10.7150/ijms.79274 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification and validation of novel signature associated with hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis using Single-cell and WGCNA analysis
1. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 230012, Hefei, China.
2. Department of oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 219 Moganshan Road, Xihu District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province 310005, China.
3. Cancer Research Centre, Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University/Beijing Tuberculosis and Thoracic Tumor Research Institute, 101149, Beijing, China.
# Hang Song, Yang Ge and Jing Xu made equal contribution to this work.
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma is a rapidly advancing malignancy with a poor prognosis. Therefore, further research is needed on its potential pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.
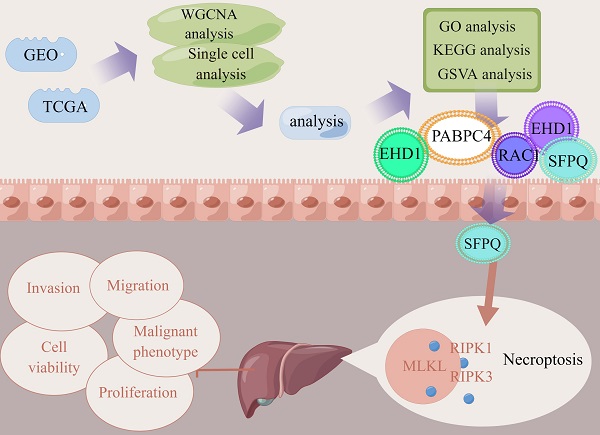
Methods: In this study, the relevant datasets were downloaded from the TCGA database and the key modules were identified using WGCNA in the necroptosis-related gene set, while single-cell datasets were scored using the necroptosis gene set. Differential genes in the high- and low-expression groups were determined using the WGCNA module genes as intersection sets to identify key genes involved in necroptosis in liver cancer. Then, prognostic models were constructed using LASSO COX regression followed by multi-faceted validation. Finally, model genes were found to be correlated with key proteins of the necroptosis pathway and used to identify the most relevant genes, followed by their experimental validation. Subsequently, on the basis of the analysis results, the most relevant SFPQ was selected for cell-level verification.
Results: We constructed a prognosis model that included five necroptosis-related genes (EHD1, RAC1, SFPQ, DAB2 and PABPC4) to predict the prognosis and survival of HCC patients. The results showed that the prognosis was more unfavorable in the high-risk group compared to the low-risk group, which was corroborated using ROC curves and risk factor plots. In addition, we further checked the differential genes using GO and KEGG analyses and found that they were predominantly enriched in the neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction pathway. The results of the GSVA analysis demonstrated that the high-risk group was mainly enriched in DNA replication, regulation of the mitotic cycle, and regulation of various cancer pathways, while the low-risk group was predominantly enriched in the metabolism of drugs and xenobiotics using cytochrome P450. SFPQ was found to be the main gene that affects the prognosis and SFPQ expression was positively correlated with the expression of RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL. Furthermore, the suppression of SFPQ could inhibit hyper-malignant phenotype HCC cells, while the WB results showed that inhibition of SFPQ expression also resulted in lower expression of necroptosis proteins, compared to the sh-NC group.
Conclusions: Our prognostic model could accurately predict the prognosis of patients with HCC to further identify novel molecular candidates and interventions that can be used as alternative methods of treatment for HCC.
Keywords: HCC, Necroptosis, Prognosis, TCGA, WGCNA

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact