3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1942-1952. doi:10.7150/ijms.77879 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Effects of Daehwang-Hwanglyoun-Sasim-Tang on brain injury and cognitive function in mice caused by bilateral common carotid artery stenosis
1. College of Korean Medicine, Dong-Eui University, Busan 47227, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts 02129, USA.
3. College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Goyang 10326, Republic of Korea.
4. School of Public Health, Far East University, Eumseong, 27601, Republic of Korea.
5. School of Korean Medicine, Pusan National University, Yangsan 50612, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
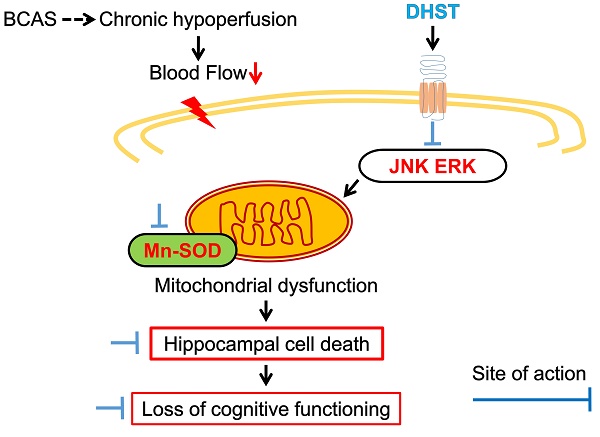
Among geriatric diseases, cerebrovascular disease ranks fourth according to the Causes of Death Statistics in 2019, Korea, and is the most common cause of acquired disorders in adults. Daehwang-Hwanglyoun-Sasim-Tang (DHST), a herbal prescription consisting of two herbal medicines, Rhei Rhizoma and Coptidis Rhizoma, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects. This study was conducted to confirm the anti-inflammatory mechanism of DHST treatment in ischemic brain injury and to confirm the role of DHST in cognitive function improvement. C57BL/6 male mice were randomly divided into four groups (sham operation, bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) control, experimental group administered 5 mL/kg DHST, experimental group administered 50 mL/kg DHST), with each group containing five mice. After 1 week, DHST was orally administered for 4 weeks, 5 days a week, and then behavioral evaluation of learning and memory was performed. In addition, morphological changes in the neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus were observed. Inflammation-related factors were evaluated using western blot analysis. In the 50 mL/kg DHST (H-DHST) group, the expression of apoptosis-related proteins was reduced and neuronal damage was suppressed in the hippocampal CA1 region. However, cognitive improvement was observed in the H-DHST group that was attributable to anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic pathways. In the 5 mL/kg DHST group, no significant effect was observed compared with the control group.
Keywords: Traditional medicine, herbal medicine, decoction, vascular dementia

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact