3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1912-1919. doi:10.7150/ijms.76725 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients Infected with the D614G Strain or Alpha Variant of COVID-19 in Taiwan: A Multi-Center Cohort Study
1. Department of Thoracic Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University, School of Medicine, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan.
3. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan.
4. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
5. Graduate Institute of Health Industry Technology, Research Center for Chinese Herbal Medicine, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
6. Department & Graduate Institute of Chemical Engineering & Graduate Institute of Biochemical Engineering, Ming Chi University of Technology, New Taipei, Taiwan.
7. School of Nursing, National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Sciences, Taipei, Taiwan.
8. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, New Taipei Municipal Tucheng Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
9. Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, New Taipei Municipal Tucheng Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
10. Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
#Contributed equally to this article as first authors.
Abstract
Objective: Direct comparison of the clinical traits of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in strain D614G, which originated from Wuhan, China, and the Alpha variant, which contains 17 mutations, infected patients could help physicians distinguish between strains and make clinical decisions accordingly. This study sought to compare the clinical characteristics and outcomes of the D614G strain and Alpha variant of SARS-COV-2 and identify the predictors for viral RNA clearance and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: This study recruited consecutive patients from four hospitals between March 1, 2020, and July 31, 2021. Demographic characteristics, laboratory results, and clinical outcomes were determined.
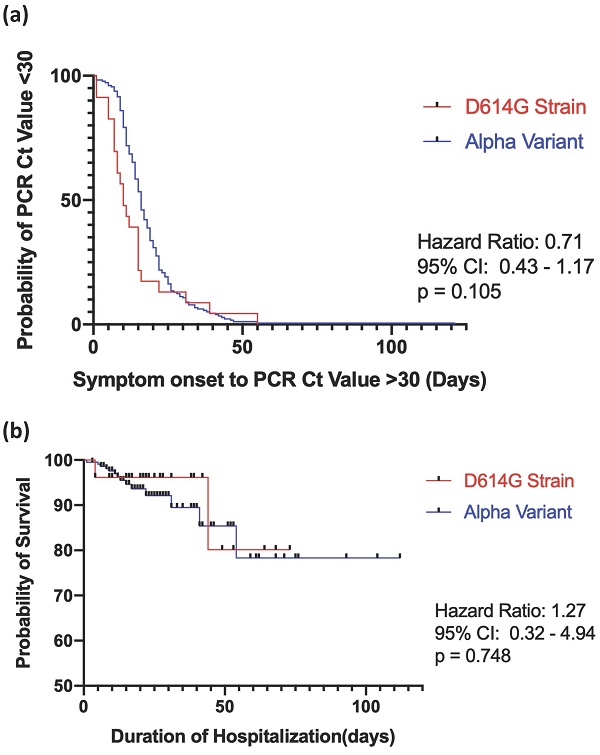
Results: Among the 239 enrolled patients, 11.2% (27/239) were infected with strain D614G and 88.7% (212/239) were infected with the Alpha variant. There were no significant differences in disease progression, rate of respiratory failure, subsequent development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute kidney injury, cardiac injury, duration of stay in the intensive care unit or hospital, discharge rate, mortality rate, or viral RNA clearance time between the two groups. Multivariate Cox regression revealed that antibiotic therapy reduced the risk of delayed viral RNA clearance (hazard ratio [HR], 0.26; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.13-0.55), while autoimmune disease increased the risk of delayed viral RNA clearance (HR, 3.98; 95% CI, 1.21-13.04). Elderly patients (age > 65 years) and patients with a history of cerebrovascular accident (CVA) were at increased risk of in-hospital mortality (HR, 5.14; 95% CI, 1.06-24.72 and HR, 3.62; 95% CI, 1.25-10.42, respectively).
Conclusions: There were no significant differences between the D614G strain and Alpha variant of COVID-19 in terms of clinical characteristics and outcomes. However, factors affecting viral RNA clearance and the risk of in-hospital mortality were identified. These results could help to inform the future prioritization of resource allocation and identify patients in need of intense monitoring.
Keywords: COVID-19, D614G, Alpha variant

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact