3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1903-1911. doi:10.7150/ijms.75337 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MMP-9/BDNF ratio predicts more severe COVID-19 outcomes
1. Medical Faculty of the Military Medical Academy, University of Defence, Crnotravska 17, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia.
2. Institute of Medical Research, Military Medical Academy, Crnotravska 17, Belgrade, Serbia.
3. Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Svetozara Markovica 69, 34000 Kragujevac, Serbia.
4. Centre for Molecular Medicine and Stem Cell Research, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Svetozara Markovica 69, 34000 Kragujevac, Serbia.
Abstract
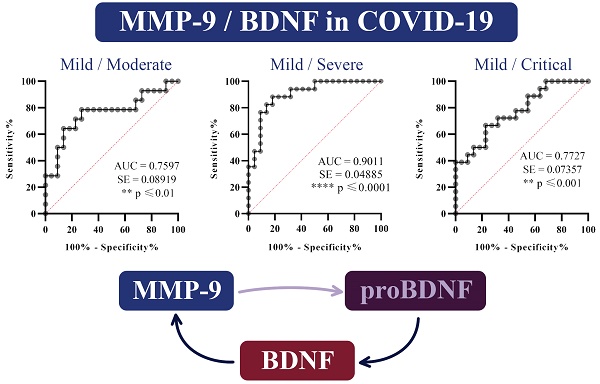
COVID-19 clinically manifests from asymptomatic to the critical range. Immune response provokes the pro-inflammatory interactions, which lead to the cytokines, reactive oxygen/nitrogen species, peptidases, and arachidonic acid metabolites enlargement and activation of coagulation components. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) contribute to tissue destruction in the development of COVID-19. Due to the endothelial, systemic course of the disease, VEGF A participates actively in COVID-19 development, while neurotrophic and metabolic effects of BDNF recommends for the prediction of complications in COVID-19 patients. Searching for a marker that would improve and simplify the ranking in COVID-19, the study intended to evaluate the relationship of MMP-9 with VEGF A, BDNF, and MMP-8 with the COVID-19 severity. Upon admission to the hospital and before the therapy administration, 77 patients were classified into a mild, moderate, severe, or critical group. Due to the inflammatory stage in COVID-19, a comparison between groups showed related differences in leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and platelets counts as anticipated. Only in seriously ill patients, there is a significant increase in the serum concentration of MMP-9, MMP-8, and VEGF A, while BDNF values did not show significant variations between groups. However, all those parameters positively correlated with each other. The ratio of MMP-9/BDNF markedly decreased in the severe and critically patients compared to the mild group. Testing the capability of this ratio to predict the COVID-19 stage by ROC curves, we found the MMP-9/BDNF could be a suitable marker for differentiating stages I/II (AUC 0.7597), stage I/III (AUC 0.9011), and stage I/IV (AUC 0.7727). Presented data describe for the first time the high-level systemic MMP-9/BDNF ratio in patients with COVID-19. This parameter could contribute to a more precise determination of the phase of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19, MMP-9, BDNF, VEGF A, MMP-8

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact