3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1879-1887. doi:10.7150/ijms.77729 This issue Cite
Research Paper
DPA promotes hBMSCs osteogenic differentiation by miR-9-5p/ERK/ALP signaling pathway
1. Stem Cell Research and Cellular Therapy Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, China.
2. Orthopedic Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, 524001, China.
3. Scientific Research Department, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, 524001, China.
#Equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
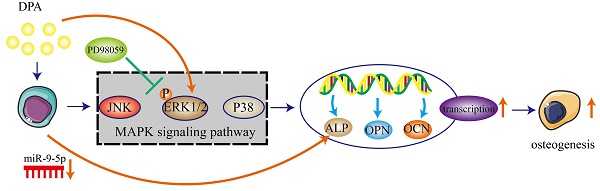
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) has been reported potentiate osteogenic differentiation, while Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), another Omega-3 fatty acid, its contribution to the osteogenic differentiation of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hBMSCs) is not entirely elucidated. The Alizarin Red S (ARS) staining and the expression of osteogenesis‑associated genes were analyzed during osteogenic induction by DPA. Then, bioinformatics analysis and dual luciferase reporter assays were investigated to confirm the interactions between miR-9-5p and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). miR-9-5p mimics / inhibitor were transfected to human hBMSCs and the osteogenic assay above was also performed. Furthermore, DPA significantly promoted the phosphorylation of ERK via miR-9-5p. PD98059, a highly specific and potent ERK1/2 inhibitor, inhibited the activation of ALP and partially reversed the role of DPA during osteogenic differentiation. These data indicated that DPA promoted osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs potentially through miR-9-5p/ERK/ALP signaling pathway, providing a potentially useful therapeutic strategy for patients to improve bone loss.
Keywords: DPA, osteogenic differentiation, hBMSCs, miR-9-5p, ERK, ALP

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact