3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(8):1340-1356. doi:10.7150/ijms.76168 This issue Cite
Review
The emerging role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of COVID-19: Protective effects of nutraceutical polyphenolic compounds against SARS-CoV-2 infection
1. Division of Chest Medicine, Kaohsiung Municipal Min-Sheng Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, ROC
2. Division of Chest Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, CHENG HSIN General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC
3. Division of Chest Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, ROC
4. Department of Clinical Pathology and Medical Research, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan, ROC
5. Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan, ROC
6. Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Fu-Jen Catholic University Hospital, School of Medicine, Fu-Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan, ROC
7. Department of Research, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan, ROC
#These authors equal contribution
Abstract
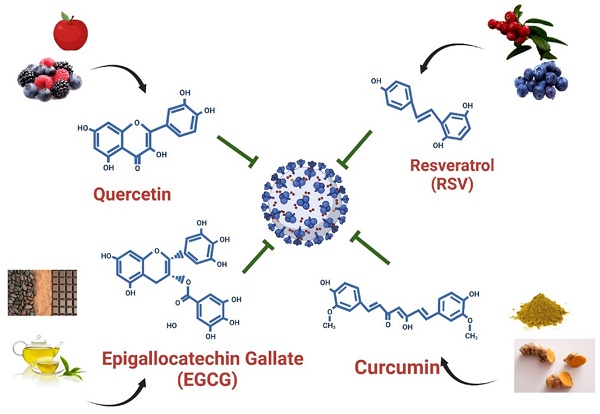
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection can cause immunosuppression and cytokine storm, leading to lung damage and death. The clinical efficacy of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs in preventing viral entry into host cells and suppressing viral replication remains inadequate. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are crucial to the immune response to and pathogenesis of coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV-2. However, the specific roles of miRNAs in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 remain unclear. miRNAs can participate in SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis through at least four possible mechanisms: 1. host cell miRNA expression interfering with SARS-CoV-2 cell entry, 2. SARS-CoV-2-derived RNA transcripts acting as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) that may attenuate host cell miRNA expression, 3. host cell miRNA expression modulating SARS-CoV-2 replication, and 4. SARS-CoV-2-encoded miRNAs silencing the expression of host protein-coding genes. SARS-CoV-2-related miRNAs may be used as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers for predicting outcomes among patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, accumulating evidence suggests that dietary polyphenolic compounds may protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection by modulating host cell miRNA expression. These findings have major implications for the future diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact