3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(8):1275-1289. doi:10.7150/ijms.73113 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification and validation of MicroRNA-mRNA Networks in Dorsal Root Ganglia after Peripheral Nerve Injury
1. Department of Orthopedics and Trauma, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing, China, 100044.
2. Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery, Center for Orthopaedic Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
3. Orthopaedic Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou, China.
* These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
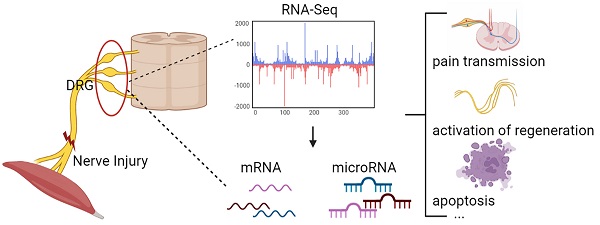
Changes in DRG after nerve injury involve neuronal damage, apoptosis, pain transmission, and activation of regenerative programs. It is unclear which genes and microRNAs may play a major role in this process. Therefore, this study performed a meta-analysis of previously published gene expression data to reveal the potential microRNA-mRNA network in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) after peripheral nerve injury. We searched 5 mRNA and 3 microRNA expression data sets, obtained 447 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 5 differentially expressed miRNAs, determined the biological pathways enriched by these DEGs, and further predicted new microRNA-mRNA interactions, such as miR-21/Hmg20a, miR-221/Ube2ql1, miR-30c-1/Rhoq, miR-500/Sema3c, and miR-551b/Cdc42se2. We verified these hub mRNA and miRNA in rats by qRT-PCR and found the results were consistent with the bioinformatics analysis. And we predicted transcription factors associated with these genes (gTFs) and TFs associated with these microRNAs (mTFs) and constructed the mTF-miRNA-gene-gTF regulatory network to further explore the molecular mechanism in DRG. Finally, we compared the DRG transcriptome after PNI to that of chronic constriction injury (CCI), and found that PNI caused greater damage to DRG compared to CCI. At the same time, the related mechanisms of pain caused by the two pathophysiological process may be different.
Keywords: transcriptome, mRNA, microRNA, transcription factors, peripheral nerve injury

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact