Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(2):310-320. doi:10.7150/ijms.68494 This issue Cite
Review
Application of dental pulp stem cells in oral maxillofacial tissue engineering
1. Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
2. Department of Oral Emergency, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
3. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
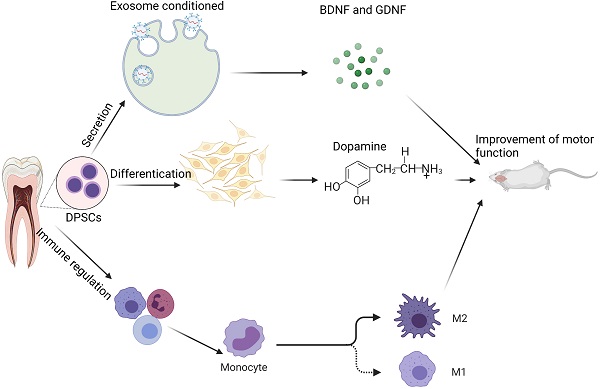
In the maxillofacial area, soft and hard tissue abnormalities are caused by trauma, tumors, infection, and other causes that expose the maxillofacial region to the surface of the human body. Patients' normal physiological function and appearance are interfered with, and their mental health is adversely impacted, reducing their overall life quality. The pursuit of appropriate medical treatments to correct these abnormalities is thus vital. Autologous stem cell regeneration technology mainly focused on tissues has lately emerged as a significant problem in the medical community. Because of the capacity of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) to self-renew, the use of DPSCs from the human pulp tissues of deciduous teeth or permanent teeth has gained popularity among scientists as a stem cell-based therapy option. Aside from that, they are simple to extract and have minimal immunogenicity. As a result, bone tissue engineering may be a critical component in treating maxillofacial and periodontal bone abnormalities. DPSCs activity in maxillofacial and periodontal tissue-engineered bone tissue was investigated in this research.
Keywords: Dental pulp stem cells, periodontal disease, tissue-engineered, osteogenic

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact