3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(15):3367-3372. doi:10.7150/ijms.62286 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Antenatal Betamethasone Induces Increased Surfactant Proteins and Decreased Foxm1 Expressions in Fetal Rabbit Pups
1. Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract
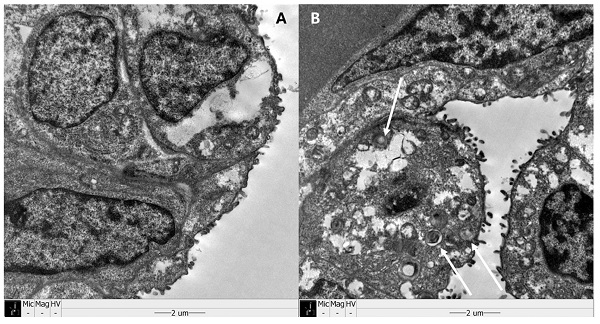
Introduction: Antenatal steroid improves respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. The molecular mechanism of the process is not well established. The aim of this study is to investigate the possible association between antenatal steroid and fetal Forkhead box M1(Foxm1) expression.
Materials and methods: An animal study using mated pregnant New Zealand white rabbits and their fetuses was designed. Fourteen mother rabbits were assigned to four groups to undergo a cesarean section. In groups 1, 2, and 3, preterm pups were harvested on day 27 of gestation. In group 4, term pups were harvested on day 31. Antenatal maternal intramuscular injection was performed in groups 2 (normal saline) and 3 (betamethasone). Using qRT-PCR and Western blot, mRNA transcription and protein expression of surfactant protein (SP) A, B, C, and Foxm1 were compared between the pups of those four groups.
Results: Sixty two fetal rabbits were harvested. One-way ANOVA test showed higher mRNA transcription of SPs in groups 3 and 4 than groups 1 and 2. Significantly lower Foxm1 mRNA transcription and protein expression were observed in group 3 or 4 compared with group 1 or 2.
Conclusion: Decreased Foxm1 expression was associated in an antenatal betamethasone animal model.
Keywords: Respiratory distress syndrome, newborn, Pulmonary surfactant, Pulmonary surfactant associated proteins, Forkhead box M1 protein, human

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact