3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3333-3341. doi:10.7150/ijms.62621 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Incidence and Effect of Cytomegalovirus Disease on Mortality in Transplant Recipients and General Population: Real-world Nationwide Cohort Data
1. Divison of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract
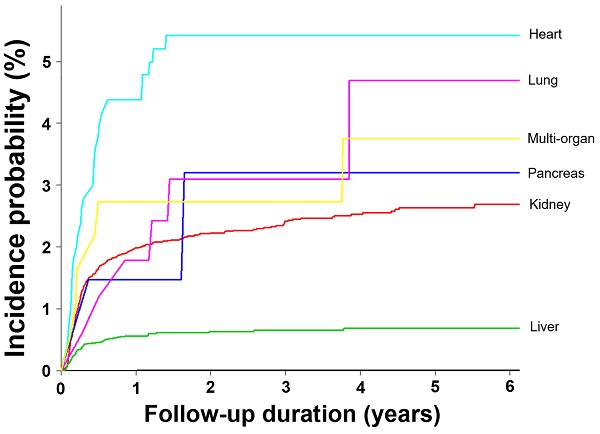
Background: In addition to the conventional opportunistic infections in solid organ transplantation (SOT) and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) recipients, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is associated with various chronic inflammatory diseases or poor outcomes in non-immunocompromised critically ill patients. To evaluate the burden or outcome of CMV replication in non-transplant individuals, we compared the incidence rates (IRs) for CMV disease and all-cause mortality between SOT recipients, HSCT recipients, and non-transplant population.
Methods: The SOT (N=16,368) and HSCT (N=10,206) cohorts between 2010 and 2015 were established using the WHO ICD-10 from the whole population-based large database of the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service (HIRA). CMV cases, defined as symptomatic disease with isolation of virus, DNA, pp65 antigen, and pathology except CMV syndrome, were extracted with the unique codes for relief of medical costs of HIRA in the same dataset. Cox's proportional hazard regression analyses and log-rank test in the Kaplan-Meier curves were performed to compare all-cause mortality between the three groups.
Results: The CMV IRs adjusted by age and sex were significantly higher in the SOT (adjusted IR [95% confidence intervals], 33.1 [28.8-38.0] per 1,000 person-years) and HSCT recipients (5.1 [4.6-6.1] per 1,000 person-years) than in the whole population (0.58 [0.49-0.67] per 100,000 person-years). However, SOT recipients with CMV (18/283, 6.4%) had significantly lower all-cause mortality than non-transplant individuals with CMV (207/1,258, 16.5%) (adjusted hazard ratio [95% CI], 0.42 [0.25-0.67], log-rank P < 0.001).
Conclusion: These data suggest that CMV disease in patients without transplants is associated with poor outcomes.
Keywords: Cytomegalovirus, Disease, Incidence, Mortality, Population, Solid organ transplantation, Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact