Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3318-3325. doi:10.7150/ijms.61329 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hydrogen Attenuates Myocardial Injury in Rats by Regulating Oxidative Stress and NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediated Pyroptosis
1. Department of Cardiology, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
2. Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Purpose: Hydrogen (H2) is an antioxidant with anti-inflammatory and apoptosis functions.This study aimed to estimate the effects of H2 on acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in rats and its association with the inhibition of oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte pyroptosis.
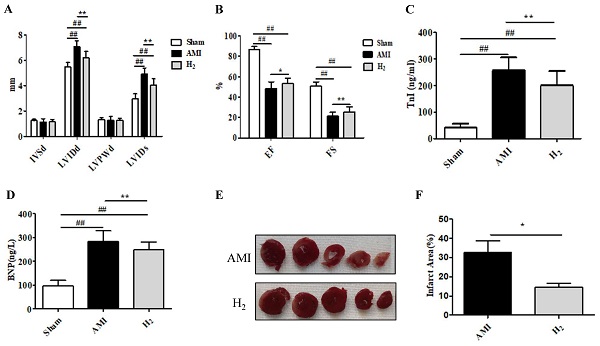
Methods: Sixty-four rats were randomly divided into three groups (Sham, AMI, and H2). The left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) of rats in the AMI and H2 groups was ligated, while rats in the Sham group were threaded without ligation. In addition, 2% H2 was administered by inhalation for 24 h after ligation in the H2 group. Transthoracic echocardiography was performed after H2 inhalation, followed by collection of the serum and cardiac tissue of all rats.
Results: H2 inhalation ameliorated the cardiac dysfunction, infarct size and inflammatory cell infiltration caused by AMI. Meanwhile, H2 inhalation reduced the concentration of serum Troponin I (TnI), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), reactive oxygen species (ROS), cardiac malondialdehyde (MDA), and 8-OHdG. In addition, H2 inhalation inhibited cardiac inflammation and pyroptosis relative proteins expression.
Conclusion: H2 effectively promoted heart functions in AMI rats by regulating oxidative stress and pyroptosis.
Keywords: hydrogen, acute myocardial infarction, oxidative stress, pyroptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact