3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3271-3279. doi:10.7150/ijms.61720 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Optimization of artificial urine formula for in vitro cellular study compared with native urine
Medical Proteomics Unit, Office for Research and Development, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10700, Thailand
Abstract
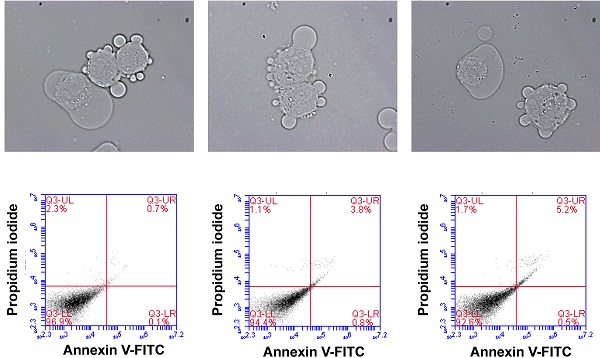
Several artificial urine (AU) formulas have been developed to mimic the normal urine. Most of them are protein-free, particularly when secreted proteins (secretome) is to be analyzed. However, the normal urine actually contains a tiny amount of proteins. We hypothesized that urinary proteins at physiologic level play a role in preservation of renal cell biology and function. This study evaluated the effects from supplementation of 0-10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) into the well-established AU-Siriraj protocol on MDCK renal tubular cells. Time to deformation (TD) was reduced by both native urine and AU-Siriraj without/with FBS compared with complete culture medium (control). Among the native urine and AU-Siriraj without/with FBS, the cells in AU-Siriraj+2.5% FBS had the longest TD. Supplementation of FBS increased cell death in a dose-dependent manner (but still <10%). Transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) of the polarized cells in the native urine was comparable to the control, whereas that of the cells in AU-Siriraj+2.5% FBS had the highest TER. These data indicate that supplementation of 2.5% FBS into AU-Siriraj can prolong time to deformation and enhance polarization of renal tubular cells. Therefore, AU-Siriraj+2.5% FBS is highly recommended for in vitro study of cell biology and function (when secretome is not subjected to analysis).
Keywords: AU-Siriraj, Cell polarization, Fetal bovine serum, Protein supplement, Renal tubular cell, Transepithelial electrical resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact