3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):3004-3013. doi:10.7150/ijms.55592 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CD8+ T cell survival in lethal fungal sepsis was ameliorated by T-cell-specific mTOR deletion
1. Department of Critical Care Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Beijing 100730, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Science; Beijing Key Laboratory for Mechanisms Research and Precision Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Diseases, Beijing 100730, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
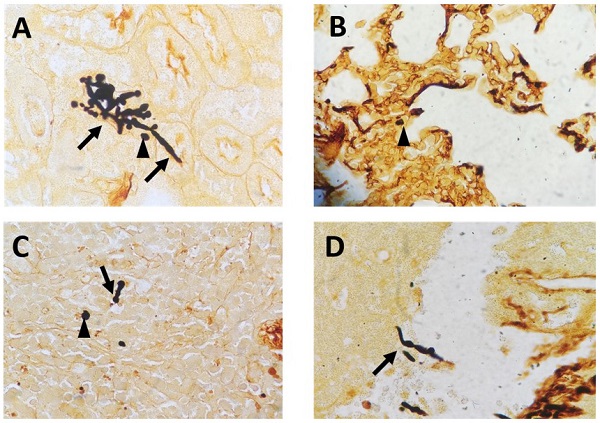
Lethal fungal sepsis causes high morbidity and mortality in intensive care patients. Fungal infections have an immunological basis, and it has been shown in recent studies that decreased CD8+ T-cell count in fungal infections is related to prognosis, while the underlying mechanism is still unclear. Here, a lethal fungal sepsis model induced by candidemia was created and we found a decreased CD8+ T-cell count and exaggerated apoptosis. Simultaneously, expression of light chain (LC)3B in CD8+ T cells increased, along with increased autophagosomes and accumulation of p62 in infected mice. We regulated the activity of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway using T-cell-specific mTOR/ TSC1 deletion mice. We observed increased number of autophagosomes and expression of LC3B in CD8+T cells after T-cell-specific mTOR knockout, while accumulation of p62 was not ameliorated, and there was no increase in the number of autolysosomes. Apoptosis rate and expression of BIM, a pro-apoptotic gene, decreased in CD8+ T cells in mTOR-deletion mice but increased in TSC1-deletion mice. Our results showed increased CD8+ T-cell death in spleen of lethal fungal sepsis mice, and decreased expression of mTOR ameliorated CD8+ T-cell survival. mTOR may be a possible target to reverse CD8+ T-cell immune dysfunction in lethal fungal sepsis.
Keywords: lethal fungal sepsis, CD8+T cell survival, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact