3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(12):2705-2715. doi:10.7150/ijms.57167 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits activation of the AIM2 inflammasome pathway and NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway by inducing autophagy in A431 human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells
1. Department of Dermatology, Cosmetology and Venereology, Shenzhen Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, 518101, Guangdong, China.
2. Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment Center for Infectious Diseases, Dermatology Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510091, Guangdong, China.
3. Department of Dermatology, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, 570311, Hainan, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
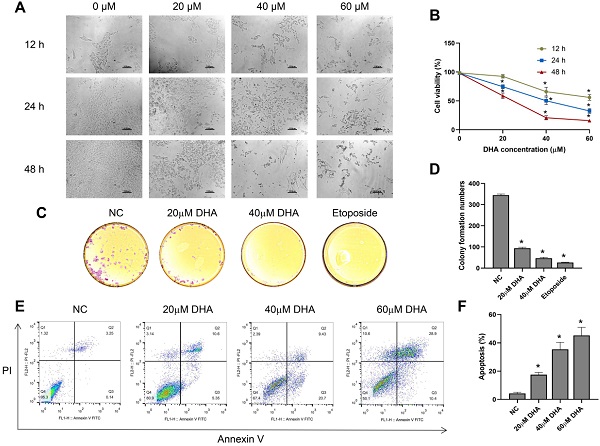
The therapeutic effect of dihydroartemisinin (DHA) against cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) has been previously demonstrated; however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. This study sought to verify the therapeutic effect of DHA against cSCC and explore its underlying mechanism in A431 cSCC cells. This study reported that DHA inhibited A431 cells proliferation in a time- and concentration-dependent manner and promoted A431 cells apoptosis. Moreover, DHA inhibited the invasion and migration of A431 cells. Mechanistically, DHA promoted autophagy and inhibited activation of the absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome pathway and NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Treatment of A431 cells with the mTOR inhibitor, and autophagy promoter, rapamycin also inhibited these two pathways. In conclusion, DHA inhibited activation of the AIM2 inflammasome pathway and NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway by promoting autophagy in A431 cells, thus accounting for its therapeutic effect. Induction of autophagy by DHA may be mediated by inhibiting the mTOR pathway and promoting reactive oxygen species production.
Keywords: dihydroartemisinin, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, autophagy, AIM2 inflammasome pathway, NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact