3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(12):2689-2696. doi:10.7150/ijms.58789 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Elevated plasma level of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in patients with breast cancer
1. Division of General Surgery, Department of Surgery, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
2. Department of Emergency, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
3. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
4. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
5. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
6. School of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
7. The School of Chinese Medicine for Post Baccalaureate, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
8. School of Medicine for International Students, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
9. Department of Nutrition, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
10. Department of Chemical Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
11. Department of Biomedical Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
12. Department of Electrical Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
13. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Dachang Hospital, Kaohsiung, 80794 Taiwan.
14. Health Examination Center, E-Da Dachang Hospital, Kaohsiung, 80794 Taiwan.
15. Lee's Endocrinology Clinic, Pingtung, 90000 Taiwan.
Abstract
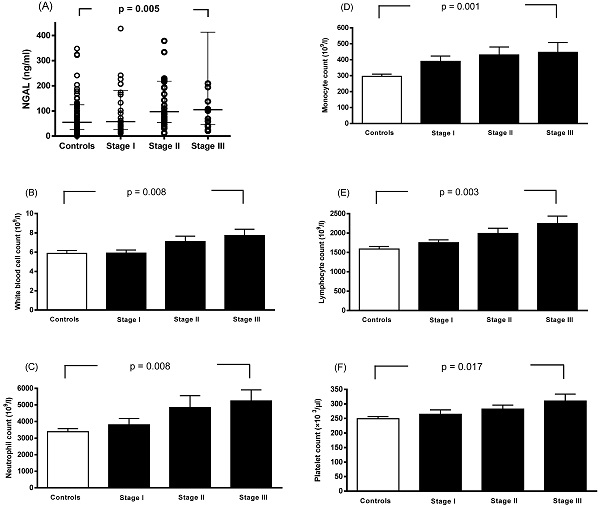
Background: Neutrophil gelatinase‑associated lipocalin (NGAL), also known as lipocalin 2, siderocalin, 24p3 or uterocalin, plays a key role in inflammation and in different types of cancer. In this study, we investigated whether plasma NGAL levels were altered in patients with breast cancer. The relationship between plasma NGAL levels and pretreatment hematologic profile was also explored.
Methods: Plasma NGAL concentrations were measured using ELISA in breast cancer patients and control subjects. A total of 75 patients with breast cancer and 65 age- and body mass index-matched control subjects were studied. All of the study subjects were female.
Results: Plasma NGAL level was found to be elevated in the patients with breast cancer compared to the control subjects (94.3 ng/mL (interquartile range 39.3-207.6) vs. 55.0 ng/mL (interquartile range 25.8-124.7), p = 0.007). Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that NGAL was independently associated with breast cancer, even after adjusting for known biomarkers. Furthermore, NGAL level was elevated in the breast cancer patients who were negative progesterone receptor status, had a histologic grade ≥ 2, clinical stage III, and pathologic stage T2+T3+T4. In addition, NGAL level was significantly correlated with white blood cell (WBC) count, monocyte count, neutrophil count, and platelet count (all p < 0.01). Moreover, WBC count, neutrophil count, monocyte count, lymphocyte count, platelet count, and NGAL level gradually increased as the stage progressed.
Conclusions: Increased plasma NGAL levels were associated with breast cancer independently of risk factors, and were correlated with inflammatory biomarkers. These results suggest that NGAL may act through inflammatory reactions to play an important role in the pathogenesis of breast cancer.
Keywords: neutrophil gelatinase‑associated lipocalin, breast cancer, white blood cell count, monocyte count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, platelet count

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact