3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(12):2545-2550. doi:10.7150/ijms.58766 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Repositive RT-PCR test in discharged COVID-19 patients during medical isolation observation
1. Department of Neurology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan province, China.
2. Department of laboratory medicine, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China.
#First authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
Objectives: The epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been researched. However, the prevalence of repositivity by real-time PCR for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) remains unclear.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted involving 599 discharged patients with COVID-19 in a single medical centre. The clinical features of patients during their hospitalization and 14-day post-discharge quarantine were collected.
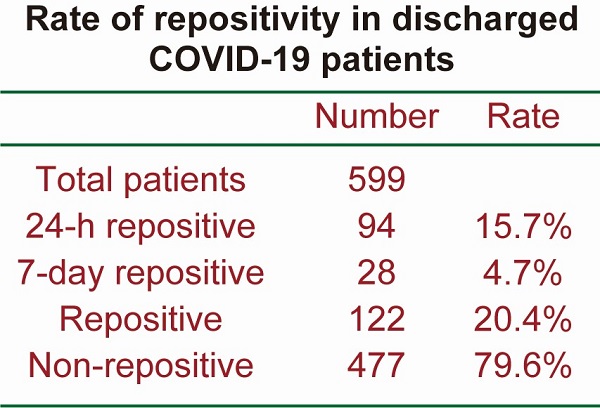
Results: A total of 122 patients (20.4%) out of 599 patients retested positive after discharge. Specifically, 94 (15.7%) retested positive within 24 h of discharge, and another 28 patients (4.7%) were repositive on day 7 after discharge, although none showed any clinical symptomatic recurrence. Both repositives and non‑repositives have similar patterns of IgG and IgM. Notably, the length of hospitalization of non-repositive patients was longer than that of 24-h repositive patients and 7-day repositive patients. In addition, the length of hospitalization of 24-h repositive patients was shorter than that of 7-day repositive patients, indicating that the length of hospitalization was also a determinant of viral shedding.
Conclusion: Our study provides further information for improving the management of recovered and discharged patients, and further studies should be performed to elucidate the infectiveness of individuals with prolonged or RNA repositivity.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), discharged patient, real-time PCR, repositive, antibody

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact