Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(8):1899-1909. doi:10.7150/ijms.54860 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ammonium Ferric Citrate induced Ferroptosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma through the inhibition of GPX4-GSS/GSR-GGT axis activity
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200433, China.
2. Department of Acupuncture, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200086, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200031, China.
4. Shanghai Geriatric Institute of Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200031, China.
*Co-first authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
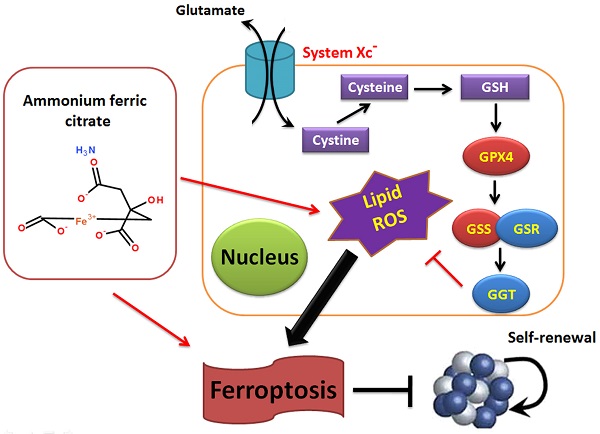
The morbidity and mortality rates associated with non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) are increasing every year, placing new demands on existing therapies and drugs. Ammonium ferric citrate (AFC) is often used as a food additive for iron supplementation; however, to our knowledge, no studies have investigated whether AFC can induce ferroptosis in NSCLC. In this study, we demonstrated that specific concentrations of AFC effectively inhibit the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cell lines in vitro using a cell proliferation inhibition test, a transwell assay, and flow cytometry analysis of cell cycle and apoptosis. In addition, AFC significantly induced oxidative stress injury in lung cancer cell lines. A quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay showed that AFC markedly reduced the expression levels of cell growth factors, negative regulators of ferroptosis, and autophagy regulators. Lastly, a protein-protein interaction analysis revealed that glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) exerted its biological role through the regulation of the GSS/GSR complex and downstream GGT family proteins. When the expression of GPX4 changes, its biological activities, such as the glutathione metabolic process, cellular biosynthetic process, cellular response to chemical stimulus, and antioxidant activity, change accordingly, thereby affecting the survival quality and physiological and biochemical activities of cells. Overall, this study verifies that AFC has the biological activity of activating oxidative stress injury in NSCLC cell lines, leading to a decrease in their autophagy and inducing ferroptosis. We also confirmed that the GPX4-GSS/GSR-GGT axis is a crucial target of AFC-induced ferroptosis.
Keywords: ammonium ferric citrate, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, autophagy, ferroptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact