3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(7):1592-1599. doi:10.7150/ijms.52405 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Optimized combination of circulating biomarkers as predictors of prognosis in AECOPD patients complicated with Heart Failure
1. Key Laboratory of Shenzhen Respiratory Diseases, Institute of Shenzhen Respiratory Diseases, Shenzhen People's Hospital (The First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology, The Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University), Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Shenzhen Respiratory Diseases, Institute of Shenzhen Respiratory Diseases, Emergency Department, Shenzhen People's Hospital (The First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology, The Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University), Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Abstract
Background: Systematic inflammation, nutritional status, and cardiovascular function have been associated with the outcomes of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) patients with heart failure (HF). However, the value of their relevant biomarkers in predicting mortality has not been well defined yet. We aimed to investigate the prognostic value of circulating biomarkers including C-reaction protein (CRP)/albumin (ALB), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) for AECOPD patients with HF.
Methods: A retrospective study was carried out in the Second Clinical College of Jinan University from January 1, 2013 to January 31, 2019. A total of 146 cases of AECOPD complicated with HF were enrolled and classified into survivor group (n=94) and non-survivor group (n=52). The baseline characteristics, CRP/ALB ratio, NLR, PLR, serum levels of NT-proBNP, and other indicators were collected. The predictors for prognosis were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression, and the ability to predict 28-day mortality was evaluated by receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC) and the area under the curve (AUC).
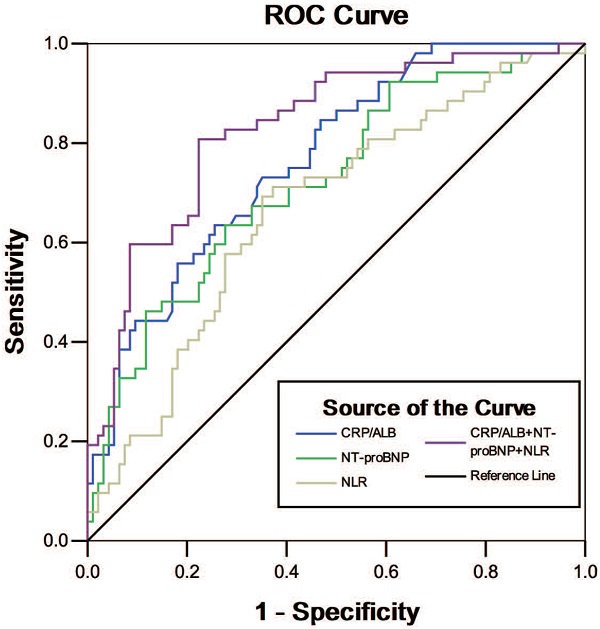
Results: The patients in non-survivors had significantly higher levels of CRP, CRP/ALB, NLR, PCT and NT-proBNP, but lower ALB levels compared to the survivors [111.7 (56.9, 186.5) VS. 43.8 (10.3, 96.1) mg/L, 4.6 (2.0, 8.0) VS. 1.4 (0.3, 3.4), 22.2 (11.1, 40.1) VS. 12.0 (6.2, 24.8), 2.6 (0.2, 10.3) VS. 0.08 (0.1, 0.5) ng/ml, 17912.5 (9344.0, 34344.5) VS. 9809.0 (4415.9, 16387.2) ng/ml, 25.8 (23.2, 30.5) VS. 30.7 (27.9, 34.1) g/L; P < 0.001, <0.001, 0.001, <0.001, <0.001, and < 0.001, respectively]. No significant difference in PLR was found between the two groups (P=0.413). The logistic analysis revealed that CRP/ALB (OR=1.303, 95%CI: 1.145-1.483, P<0.001), NT-proBNP (OR=1.041, 95%CI: 1.010-1.073, P=0.009) and NLR (OR=1.010, 95%CI: 0.999-1.022, P<0.001) are independent risk factors for predicting the 28-day mortality. The AUC of the ROC curves were 0.768, 0.767, 0.757, 0.723, 0.716, and 0.668 for CRP/ALB, PCT, CRP, NT-proBNP, ALB, and NLR, respectively. The combination of CRP/ALB, NLR and NT-proBNP as biomarkers was shown to have better accuracy for predicting prognosis (AUC=0.830, 95%CI: 0.761-0.899, P<0.001), with a higher specificity of 80.8% and specificity of 77.7% as compared with each single biomarkers.
Conclusions: High levels of NLR, CRP/ALB and NT-proBNP may be clinical usefully predictors for death in AECOPD patients with HF. Combination of NLR with CRP/ALB and NT-proBNP can provide a higher accuracy for predicting 28-day mortality in these patients.
Keywords: acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure, C-reaction protein/albumin ratio, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, prognosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact