3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1277-1284. doi:10.7150/ijms.51279 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Longitudinal changes in COVID-19 clinical measures and correlation with the extent of CT lung abnormalities
1. Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
2. Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Wuhan, Hubei, China
3. Cancer Center, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
4. Center for Clinical Spectroscopy, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
* These authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Abstract
Rationale: To assess the longitudinal changes and relationships of clinical measures and extent of CT lung abnormalities in COVID-19.
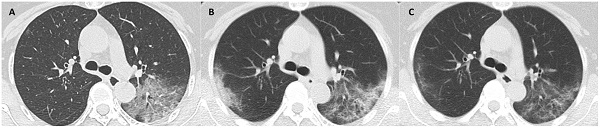
Methods: 81 patients with COVID-19 were prospectively enrolled and followed until discharge. CT scores were quantified on a basis of a CT scoring system where each lung was divided into 3 zones: upper (above the carina), middle, and lower (below the inferior pulmonary vein) zones; each zone was evaluated for percentage of lung involvement on a scale of 0-4 (0, 0%; 1, 0-24%; 2, 25% - 49%; 3, 50% -74%; 4, >74%).Temporal trends of CT scores and the laboratory parameters characteristic of COVID-19 were analyzed. Correlations between the two were determined at three milestones (initial presentation, worst CT manifestation, and recovery finding before discharge). Their correlations with duration to worst CT manifestation and discharge from symptom onset were evaluated.
Results: CT scores peaked during illness days 6-11 (median: 5), and stayed steady. C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase increased, peaked on illness days 6-8 and 8-11 (mean: 23.5 mg/L, 259.9 U/L), and gradually declined. Continual decrease and increase were observed in hemoglobin and lymphocyte count, respectively. Albumin reduced and remained at low levels with a nadir on illness days 12-15 (36.6 g/L). Both initial (r = 0.58, 0.64, p < 0.05) and worst CT scores (r = 0.47, 0.65, p < 0.05) were correlated with C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase; and CT scores before discharge, only with albumin (r = -0.41, p < 0.05). Duration to worst CT manifestation was associated with initial and worst CT scores (r = 0.33, 0.29, p < 0.05). No parameters were related to timespan to discharge.
Conclusion: Our results illustrated the temporal changes of characteristic clinical measures and extent of CT lung abnormalities in COVID-19. CT scores correlated with some important laboratory parameters, and might serve as prognostic factors.
Keywords: corona virus disease 2019, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, CT, laboratory parameters, longitudinal changes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact