3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1207-1215. doi:10.7150/ijms.47494 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of parameters in routine blood and coagulation tests related to the severity of COVID-19
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China.
2. Department of Integrative Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China.
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify the predictive value of simple markers in routine blood and coagulation tests for the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: A total of 311 consecutive COVID-19 patients, including 281 patients with mild/moderate COVID-19 and 30 patients with severe/life-threatening COVID-19, were retrospectively enrolled. Logistic modeling and ROC curve analyses were used to assess the indexes for identifying disease severity.
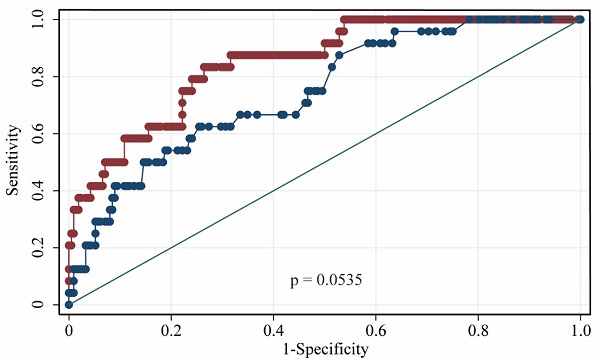
Results: Lymphocyte and eosinophil counts of COVID-19 patients in the severe/life-threatening group were significantly lower than those of patients in the mild/moderate group (P < 0.001). Coagulation parameters, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels and procalcitonin levels were higher in the severe/life-threatening group compared with the mild/moderate group (all P < 0.05). Univariate and multivariate logistic models revealed that hsCRP and fibrinogen degradation products (FDPs) were predictors of severe COVID-19 (OR = 1.072, P = 0.036; and OR = 1.831, P = 0.036, respectively). The AUROCs of hsCRP and FDP for predicting severe/life-threatening COVID-19 were 0.850 and 0.766, respectively. The optimal cutoffs of hsCRP and FDP for the severe/life-threatening type of COVID-19 were 22.41 mg/L and 0.95 µg/ml, respectively.
Conclusion: Serum CRP and FDP levels are positively related to the severity of COVID-19. This finding indicates that CRP and FDP levels may potentially be used as early predictors for severe illness and help physicians triage numerous patients in a short time.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19, highly sensitive C-reactive protein, FDP, fibrinogen degradation products

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact