3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1137-1142. doi:10.7150/ijms.51672 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Virus discharge and initial gastrointestinal involvement are inversely associated with circulating lymphocyte count in COVID-19
1. Department of Radiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Yuying Chilldren's Hospital, Wenzhou, China
2. MAFLD Research Center, Department of Hepatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
3. Department of Infectious Disease, the Sixth People's Hospital of Wenzhou, China
4. Department of Laboratory Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Yuying Children's Hospital, Wenzhou, China
#Co-first authors: Wei Chen and Kenneth I. Zheng.
Abstract
Background: It's reported SARS-CoV-2 could transmit via gastrointestinal tract, with or without pulmonary symptoms. However, as far as we know, there is no effective marker to predict the virus discharge in stool and initial gastrointestinal involvement of COVID-19 patients.
Aims: We aimed to investigate the likely biomarker predicting virus discharge in stool and initial gastrointestinal involvement of COVID-19, which may assist the clinicians in better preventing COVID-19 spread.
Methods: The patients complained of gastrointestinal symptoms, including vomiting, diarrhea, with or without respiratory symptoms, attending the Sixth People's Hospital of Wenzhou, and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, were screened by qRT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2. The confirmed COVID-19 patients, without any history of intaking contaminated food or water, were all enrolled to investigate the association between circulating lymphocyte count and virus discharge, initial gastrointestinal involvement.
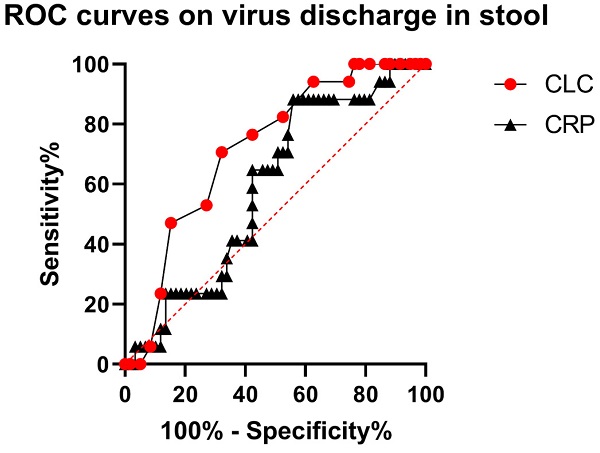
Results: Seventy-six COVID-19 patients were included in the final analysis (mean age of 44.5 years, male 44.7%), with 24 (31.5%) complained of initial gastrointestinal symptoms. Significantly lower circulating lymphocyte count was found in the patients with positive results of qRT-PCR on stool (p = 0.012). Patients were divided into tertile groups by circulating lymphocyte count: lymphocyte ≤0.88*10^9/l ( n = 25 ), 0.88*10^9/l -1.2*10^9/l ( n = 28 ), and >1.2*10^9/l ( n = 23 ), respectively. When circulating lymphocyte count increased from 1st tertile to the 2nd and 3rd tertiles, the risk of initial gastrointestinal symptoms decreased by nearly 75% (OR = 0.25, 95% CI: 0.07, 0.98, p = 0.047), 83% (OR = 0.17, 95% CI: 0.05, 0.63, p = 0.008), after adjusting for likely confounders.
Conclusions: The circulating lymphocyte count is inversely associated with virus discharge in stool, and the risk of initial gastrointestinal involvement in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: circulating lymphocyte count, COVID-19, gastrointestinal tract, CRP, stool, emergency

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact