3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1104-1113. doi:10.7150/ijms.52691 This issue Cite
Review
Macrophage Polarization and Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Department of Liver Surgery, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
*Hai Wang and Zhifeng Xi contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
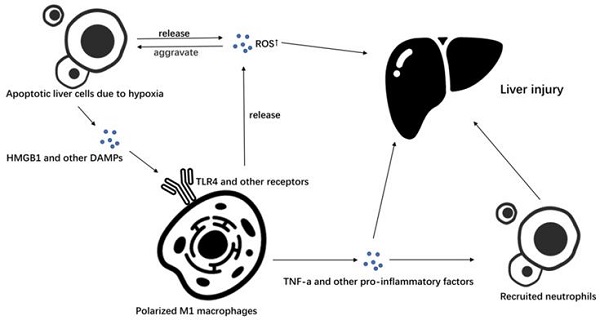
Ischemia-reperfusion injury refers to organ damage caused by the previous insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients and the involvement of metabolic by-products after blood flow is restored. Liver ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) has become a hot research in recent years, because it occurs in many clinical scenarios. After the introduction of liver transplantation and vascular control techniques in liver surgery, liver ischemia-reperfusion injury is considered to be an important factor affecting postoperative mortality and morbidity. As the largest immune organ in the human body, liver contain a lot of immune cells such as resident macrophages (Kupffer cells), dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and natural killer T cells which play a key role in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Among those, macrophage-mediated excessive inflammatory response is considered to be an important factor in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. The prominent feature of liver injury is an increase in the number of macrophages in liver due to the infiltration of blood monocytes and differentiation into monocyte-derived macrophages. Liver macrophages can be divided into M1 macrophages which can promote inflammation progress and M2 macrophages that inhibit inflammation progress according to their different phenotypes and functions. Both of them can regulate liver aseptic inflammation, and play an important role in triggering, maintaining, and improving liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. This review summarizes studies of macrophage polarization on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in recent years, to provide potential ideas for translation application in future clinical management.
Keywords: liver, ischemia-reperfusion injury, macrophage polarization

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact