ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(6):1091-1102. doi:10.7150/ijms.94644 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Development of a Novel Nomogram to Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Chronic Total Occlusion
Center for Coronary Artery Disease (CCAD), Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing Institute of Heart, Lung and Blood Vessel Diseases, Beijing 100029, China.
Abstract
Objectives: To create a nomogram using single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) myocardial perfusion imaging and 18F-FDG positron emissions tomography (PET) gated myocardial metabolism imaging to forecast major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in chronic total occlusion (CTO) patients treated with optimal medical therapy (OMT).
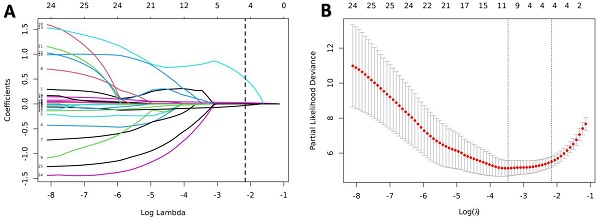
Methods: A total of 257 patients who received OMT between January 2016 and December 2021 were included in this retrospective study. Patients were randomly divided into development (n=179) and validation (n=78) cohorts. A thorough evaluation was conducted, encompassing clinical features and imaging analysis, which involved assessing myocardial perfusion and metabolism. Independent risk factors were identified using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Calibration curves and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the clinical usefulness.
Results: In the development cohort, 53 patients (29.6%) experienced MACE out of 179 patients, while in the validation cohort, MACE occurred in 23 (29.5%) patients out of 78. The PET-left ventricular end-systolic volume (P-ESV) (HR 1.01; 95% CI 1.003-1.017; p=0.003), hibernating myocardium / total perfusion defect (HM/TPD) (HR 1.053; 95% CI 1.038-1.069; p<0.001), PET-left ventricular ejection fraction (P-LVEF) (HR 0.862; 95% CI 0.788-0.943; p=0.001), and left anterior descending branch (LAD) (HR 2.303; 95% CI 1.086-4.884; p=0.03) were significantly associated with MACE and were used to develop the nomogram. The nomogram demonstrated excellent discrimination with C-indexes of 0.931 and 0.911 in the development and validation cohorts. DCA determined that the model exhibited a considerably superior net advantage in predicting MACE.
Conclusion: A new nomogram integrating clinical factors and imaging features was created to predict the risk of MACE in patients with CTO.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease, Nomogram, Myocardial Metabolism Imaging, Positron-Emission Tomography
