3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(6):1079-1090. doi:10.7150/ijms.93510 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Novel kinase 1 regulates CD8+T cells as a potential therapeutic mechanism for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
1. School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
2. The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi 530021, China.
3. Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction Faculty of Medicine Imperial College London Chelsea & Westminster Hospital, London SW10 9NH, UK.
4. Life Science and Clinical Research Center, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities,18 Zhongshan Road II, Baise 533000, Guangxi, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered co - first authors.
Abstract
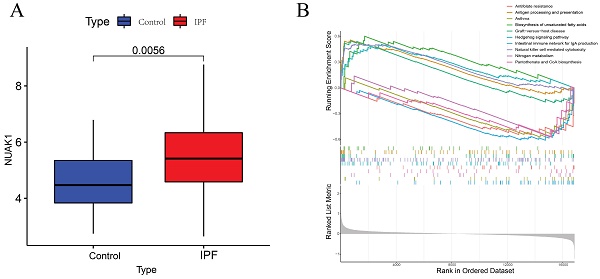
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a rare, chronic and progressively worsening lung disease that poses a significant threat to patient prognosis, with a mortality rate exceeding that of some common malignancies. Effective methods for early diagnosis and treatment remain for this condition are elusive. In our study, we used the GEO database to access second-generation sequencing data and associated clinical information from IPF patients. By utilizing bioinformatics techniques, we identified crucial disease-related genes and their biological functions, and characterized their expression patterns. Furthermore, we mapped out the immune landscape of IPF, which revealed potential roles for novel kinase 1 and CD8+T cells in disease progression and outcome. These findings can aid the development of new strategies for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of IPF.
Keywords: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, bioinformatics, immune landscape, NUAK1, CD8+T

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact