ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(2):299-305. doi:10.7150/ijms.90086 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association between hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic diseases: a multi-center, propensity-score-matched cohort study
1. Evidence-based Medicine Center, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
2. Library, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
3. School of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
4. Department of Pharmacy, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
5. Department of Pharmacology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
6. Division of Gastroenterology, Children's Medical Center, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
7. Department of Post-Baccalaureate Medicine, College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan.
8. Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Massachusetts General Hospital for Children, Boston, MA, USA
9. Institute of Medical Education, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan, Taiwan
*Dr. Meng-Che Wu and Mr. Shuo-Yan Gau contributed equally and equally share the corresponding authorship.
Abstract
Background: Cross-sectional evidence has suggested a high prevalence of atopic diseases in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). However, there is a lack of evidence based on longitudinal studies. This study aimed to assess the risk of different atopic diseases, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis, in patients with HS.
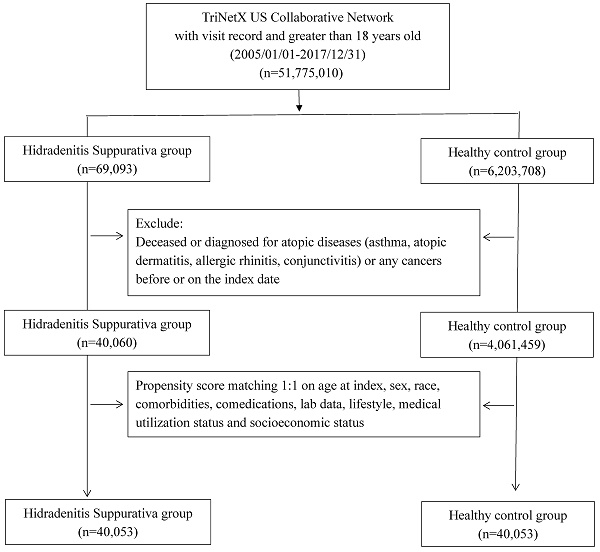
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, data from the TriNetX research network were obtained. Patients with HS were enrolled, and a 1:1 propensity score matching was performed to select a non-HS control group. Matching covariates included age, sex, race, comorbidities, comedications, socioeconomic status, lab data, and medical utilization status. Hazard ratios (HR) for atopic diseases were assessed.
Results: Over a 15-year follow-up period, patients with HS were found to be at a higher risk for atopic dermatitis (HR = 1.65; 95% CI, 1.44-1.90), asthma (HR = 1.41; 95% CI, 1.33-1.49), and allergic rhinitis (HR = 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.13). A similar trend was observed in shorter follow-up periods. The association between HS, atopic dermatitis, and asthma was consistent across different age and sex subgroups.
Conclusion: Atopic diseases including atopic dermatitis, asthma and allergic rhinitis are associated with HS. Further investigation is needed to assess the necessity of early screening for atopic diseases in patients with HS.
Keywords: hidradenitis suppurativa, atopic dermatitis, cohort, epidemiology, electronic medical records
