3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2025; 22(3):482-507. doi:10.7150/ijms.99159 This issue Cite
Review
A Mechanistic Review on Toxicity Effects of Methamphetamine
1. Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 56000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2. Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, Warneford Hospital, Oxford OX3 7JX, UK.
3. Physiology Division, Department of Medical Physiology and Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya 60132, Indonesia.
4. Old Road Campus Research Building, Department of Oncology, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7DQ, UK.
5. Institute of Molecular Biology & Biotechnologies, Ministry of Science and Education of the Republic of Azerbaijan, 11 Izzat Nabiyev Str., AZ1073, Baku, Azerbaijan.
6. Oxford Vaccine Group, Department of Paediatrics, University of Oxford, OX3 7TY, UK.
7. Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Pulau Pinang, Kampus Bertam, 13200 Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
Abstract
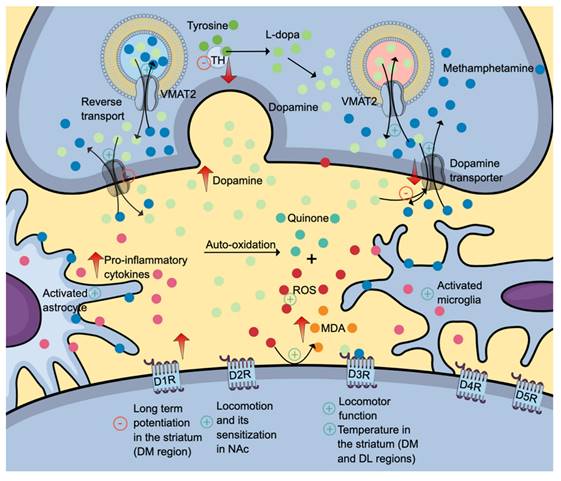
Persistent methamphetamine use causes many toxic effects in various organs, including the brain, heart, liver, kidney and eyes. The extent of its toxicity depends on numerous pharmacological factors, including route of administration, dose, genetic polymorphism related to drug metabolism and polysubstance abuse. Several molecular pathways have been proposed to activate oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis: B-cell lymphoma protein 2 (Bcl-2)-associated X (Bax)/Bcl2/caspase-3, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/p70S6K, trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1)/cAMP/lysyl oxidase, Sigmar1/ cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)/mitochondrial fission-1 protein (Fis1), NADPH-Oxidase-2 (NOX-2), renal autophagy pathway, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/ protein kinase B (Akt)/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), Nupr1/Chop/P53/PUMA/Beclin1 and Toll-like receptor (TLR)4/MyD88/TRAF6 pathways. The activation promotes pathological changes, including the disruption of the blood-brain barrier, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, acute liver failure, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, keratitis, retinopathy and vision loss. This review revisits the pharmacological profiles of methamphetamine and its effects on the brain, heart, liver, eyes, kidneys and endothelium. Understanding the mechanisms of methamphetamine toxicity is essential in developing treatment strategies to reverse or attenuate the progress of methamphetamine-associated organ damage.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, renal, meth, neurotoxicity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact