3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(9):1622-1628. doi:10.7150/ijms.92107 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Influence of the Energy Intake Variability During the Week on the Body Composition in an Adult Population
1. Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University, Kamenice 753/5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic
2. Independent Researcher
Abstract
Background: The regularity of eating, together with other nutritional factors, is one of the important determinants of health. According to previous studies, it is not clear if a greater fluctuation in energy intake is associated with higher body fat and weight gain, or if the weight of people is stable despite these fluctuations in the energy intake. The aim of the study was to verify if a higher variability in the energy intake each day of the week is related to the amount of body fat and other anthropometric parameters.
Methods: A total of 220 (151 women, 69 men) individuals of Czech Caucasian origin with a BMI of 18.3-58 kg/m2, aged 21.7-79.7 were included in the study. Selected anthropometric characteristics were measured using a bioelectrical impedance analysis. 7-day food records were completed and analyzed using nutritional software. The measured values were statistically evaluated by multiple linear regression analysis.
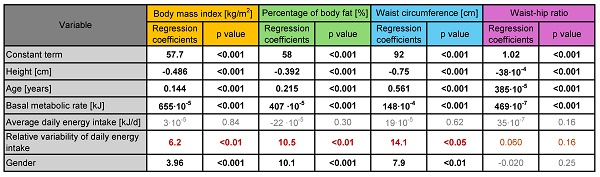
Results: The results of the multiple linear regression showed the statistically significant dependence of the percentage of body fat (p<0.01), BMI (p<0.01), and waist circumference (p<0.05) on the relative variability of the daily energy intake.
Conclusions: The results of our study suggest that people with more regular energy intake also have better anthropometric parameters related to their cardiometabolic health.
Keywords: energy intake, variability in energy intake, percentage of body fat, BMI, 7-day food records, bioelectrical impedance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact