3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(9):1604-1611. doi:10.7150/ijms.94677 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ophthalmic Artery Morphology and Hemodynamics Associated with White Matter Hyperintensity
1. Department of Ophthalmology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China.
2. Institute of Ophthalmology, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
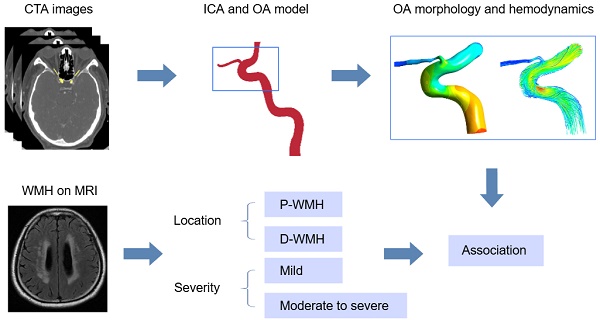
Purpose: To investigate morphological and hemodynamic characteristics of the ophthalmic artery (OA) in patients with white matter hyperintensity (WMH), and the association of the presence and severity of WMH with OA characteristics.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 44 eyes of 25 patients with WMH and 38 eyes of 19 controls. The Fazekas scale was adopted as criteria for evaluating the severity of white matter hyperintensities. The morphological characteristics of the OA were measured on the basis of three-dimensional reconstruction. The hemodynamic parameters of the OA were calculated using computational fluid dynamics simulations.
Results: Compared with the control group, the diameter (16.0±0.27 mm vs. 1.71±0.18 mm, P=0.029), median blood flow velocity (0.12 m/s vs. 0.22 m/s, P<0.001), mass flow ratio (2.16% vs. 3.94%, P=0.012) and wall shear stress (2.65 Pa vs. 9.31 Pa, P<0.001) of the OA in patients with WMH were significantly decreased. After adjusting for confounding factors, the diameter, blood flow velocity, wall shear stress, and mass flow ratio of the OA were significantly associated with the presence of WMH. Male sex and high low-density protein level were associated with moderate-to-severe total WMH, and smoking was associated with the moderate-to-severe periventricular WMH.
Conclusions: The diameter, blood flow velocity, mass flow ratio, and wall shear stress of the OA were independently associated with the presence of WMH. Atherosclerosis might be involved in the common mechanism of the occurrence of WMH and the OA changes.
Keywords: white matter hyperintensity, ophthalmic artery, hemodynamics, computational fluid dynamics

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact