3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(7):1307-1320. doi:10.7150/ijms.96274 This issue Cite
Review
Cross-Talk between the TGF-β and Cell Adhesion Signaling Pathways in Cancer
1. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Diagnostics, Dongguan Key Laboratory of Medical Bioactive Molecular Developmental and Translational Research, The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan, Guangdong, 523808, China.
2. Institute of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medical Technology, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan, Guangdong, 523808, China.
3. Department of Pathology, Binhaiwan Central Hospital of Dongguan, Dongguan, Guangdong, 523905, China.
4. School of Biomedical Engineering, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan, Guangdong, 523808, China.
† These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
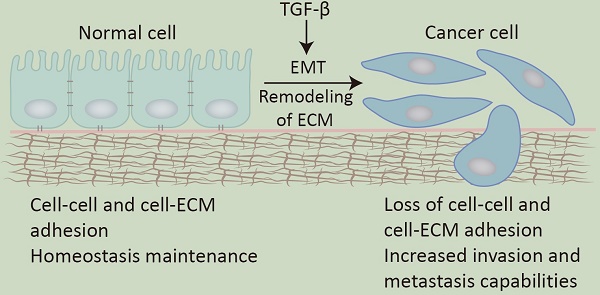
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is strongly associated with the cell adhesion signaling pathway in cell differentiation, migration, etc. Mechanistically, TGF-β is secreted in an inactive form and localizes to the extracellular matrix (ECM) via the latent TGF-β binding protein (LTBP). However, it is the release of mature TGF-β that is essential for the activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway. This progress requires specific integrins (one of the main groups of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)) to recognize and activate the dormant TGF-β. In addition, TGF-β regulates cell adhesion ability through modulating CAMs expression. The aberrant activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway, caused by abnormal expression of key regulatory molecules (such as Smad proteins, certain transcription factors, and non-coding RNAs), promotes tumor invasive and metastasis ability via epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during the late stages of tumorigenesis. In this paper, we summarize the crosstalk between TGF-β and cell adhesion signaling pathway in cancer and its underlying molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: TGF-β signaling pathway, cell adhesion signaling pathway, cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact