3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(7):1302-1306. doi:10.7150/ijms.93822 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Effect of spectacle correction on hyperopic children
1. Department of Urology, Shuang Ho Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
2. Department of Urology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
3. Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
4. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
5. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Shuang Ho Hospital, Taipei Medical University, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
6. TMU Research Center of Urology and Kidney, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
7. Beauty-Bright Eye Clinics, Zhubei City, Hsinchu County, Taiwan.
8. Department of Optometry, University of Kang Ning, Taipei, Taiwan.
9. School of Public Health, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
10. Department of Ophthalmology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
11. Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
12. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Shuang Ho Hospital, Taipei Medical University, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
13. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
14. Graduate Institute of Aerospace and Undersea Medicine, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
15. Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
16. Department of Urology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center.
Abstract
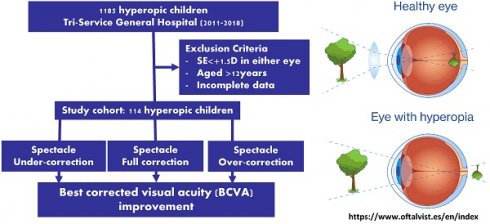
Background: Hyperopia is a significant refractive error in children, often leading to vision impairment. This study aimed to investigate whether partial or full spectacle correction is benefit for hyperopia in preschool-aged children.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on hyperopic children visited to teaching medical center outpatient clinic between October 2011 and October 2018, and were categorized into three groups: full correction, overcorrection, and undercorrection. The study was approved by the institutional ethical committee of Tri-Service General Hospital.
Results: Following a minimum of one-year follow-up period, no statistically significant differences were observed in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) among children receiving full, over, or under spectacle correction. Notably, the overcorrection group exhibited a significant reduction in spherical equivalent (SE) compared to both the full and under correction groups, indicating a better SE with spectacle overcorrection.
Conclusions: Spectacle overcorrection may offer potential benefits for enhancing SE in preschool children with hyperopia. Nevertheless, further investigation through randomized controlled trials is warranted to establish the validity of this approach and its impact on visual outcomes in this hyperopic pediatric population.
Keywords: Hyperopia, Spherical equivalent, Visual acuity, Spectacle correction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact