3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(7):1213-1226. doi:10.7150/ijms.93423 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals a Novel Prognostic Model for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
1. The Second Clinical Medical College, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, 325088, China
2. Department of Medical Oncology, the Second Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310053, China.
3. Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Diagnosis and Treatment Technology on Thoracic Oncology, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022, China.
4. The Cancer Research Institute, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022, China.
# These authors contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
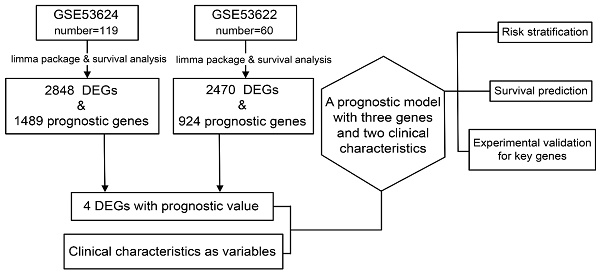
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), a gastrointestinal cancer, is associated with poor prognosis. Prognostic models predict the likelihood of disease progression and are important for the management of patients with ESCC. The objective of this study was to develop a prognostic model for ESCC using bioinformatics analysis.
Methods: Two transcriptome microarray Gene Expression Omnibus ESCC datasets (GSE53624 and GSE53622) were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using the R package limma, and genes associated with survival outcomes in both datasets were identified by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Genes with diagnostic or prognostic value were selected for further analysis, and hazard ratios and their relationship with pathological TNM (pTNM) staging were investigated using univariate and multivariate Cox analysis. After selecting the independent factors from pTNM staging, Cox analysis and nomogram plotting were performed. The ability of the model to stratify risk and predict survival was evaluated and compared with the pTNM staging system to determine its potential clinical value. Key genes were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR.
Results: Four candidate genes (B3GNT3, MACC1, NELL2, and USH1G) with prognostic value were identified from the two transcriptome microarray datasets. Age, pTNM stage, and B3GNT3, MACC1, and NELL2 were identified as independent factors associated with survival in the multivariate Cox analysis and used to establish a prognostic model. The model demonstrated significantly higher accuracy in predicting 3-year survival than the pTNM staging system and was useful for further risk stratification in patients with ESCC. B3GNT3 was significantly downregulated in ESCC tumor tissues and negatively associated with lymph node metastasis. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that B3GNT3 may play a role in immune regulation by regulating M2 macrophages.
Conclusion: This study developed a new prognostic model for ESCC and identified B3GNT3 as a potential biomarker negatively associated with lymph node metastasis, which warrants further validation.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), bioinformatics analysis, prognosis, B3GNT3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact