3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(7):1204-1212. doi:10.7150/ijms.95624 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting Cancer Mitochondria by Inducing an Abnormal Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response Leads to Tumor Suppression
1. Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
2. School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
Abstract
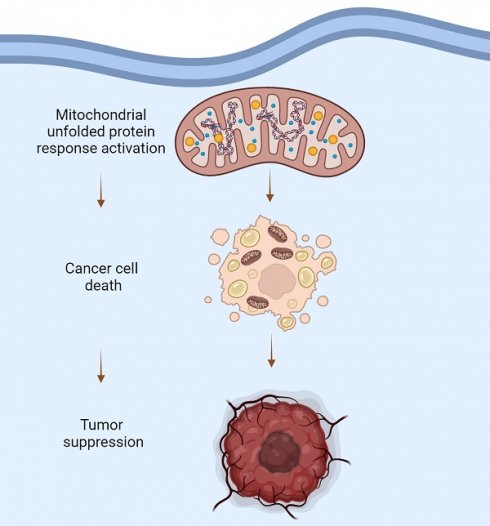
The mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) is a pivotal cellular mechanism that ensures mitochondrial homeostasis and cellular survival under stress conditions. This study investigates the role of UPRmt in modulating the response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced stress. We report that the inhibition of UPRmt via AEB5F exacerbates cisplatin cytotoxicity, as evidenced by increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and apoptosis, characterized by a surge in TUNEL-positive cells. Conversely, the activation of UPRmt with oligomycin attenuates these effects, preserving cell viability and reducing apoptotic markers. Immunofluorescence assays reveal that UPRmt activation maintains mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP production in the presence of cisplatin, countering the rise in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibiting caspase-9 activation. These findings suggest that UPRmt serves as a cytoprotective mechanism in cancer cells, mitigating cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. The data underscore the therapeutic potential of modulating UPRmt to improve the efficacy and reduce the side effects of cisplatin chemotherapy. This study provides a foundation for future research on the exploitation of UPRmt in cancer treatment, with the aim of enhancing patient outcomes by leveraging the cellular stress response pathways.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, mitochondrial unfolded protein response, mitochondria, cisplatin, oxidative stress

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact