3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(7):1187-1193. doi:10.7150/ijms.95653 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Evaluation of QRS duration and presence of fragmented QRS in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Ankara Yildirim Beyazit University Yenimahalle Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
3. Department of Cardiology, Gazi University School of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
4. Department of Gastroenterology, Ankara Yildirim Beyazit University School of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is mostly characterized by gastrointestinal tract involvement, however can also be accompanied with cardiac manifestations. QRS prolongation and the presence of QRS fragmentation (fQRS) have been previously evaluated in many chronic inflammatory diseases, as an independent predictor of cardiac events. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the QRS duration and fQRS in patients with IBD.
Methods: The presented study was designed as a single-center retrospective cohort study. The study population consisted of 217 patients with IBD and 195 healthy controls. QRS duration and presence of fQRS were evaluated using a 12-lead electrocardiogram. These parameters were compared between groups.
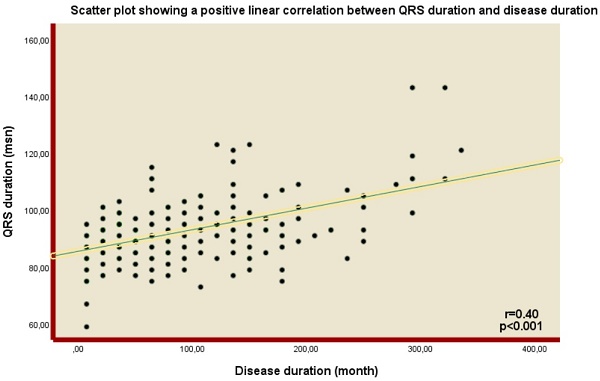
Results: QRS duration was demonstrated to be higher in the IBD group compared to the control group (92 (86-98) vs. 82 (75-90), p<0.001). The presence of fQRS was significantly higher in the IBD group (n=101 (47%) vs n=59 (30%), p=0.006). In addition, a positive correlation was demonstrated between QRS duration and disease duration (Spearman's Rho= 0.4, p<0.001). Notably, disease and QRS duration were significantly higher in the fQRS (+) group (102 (56.5-154) vs. 55 (24.3-118.3), <0.001; 94 (86-100) vs. 92 (84-96), 0.016; respectively).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that QRS prolongation and the presence of fQRS (+) were more common in IBD patients, and associated with longer disease duration. These findings may indicate subclinical cardiac involvement in IBD. Therefore, IBD patients, especially those with long-standing disease, should be followed more closely in terms of cardiac manifestations.
Keywords: cardiac arrhythmia, electrocardiogram, fragmented QRS, inflammatory bowel disease, QRS duration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact