3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(5):914-920. doi:10.7150/ijms.91607 This issue Cite
Research Paper
High-Flow Nasal Oxygen versus Conventional Nasal Cannula in Preventing Hypoxemia in Elderly Patients Undergoing Gastroscopy with Sedation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Anesthesiology, People's Hospital of Shigatse City, Tibet, China.
3. Department of Surgical Intensive Care Unit, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
4. Department of Gastrointestinal endoscopy, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
5. Department of Oncology, Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
#First authors: Xin Yin and Wen Xu contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: We aimed to compare the prevention of hypoxemia using High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) or regular nasal tubing (CNC) in elderly patients undergoing gastroscopy with sedation.
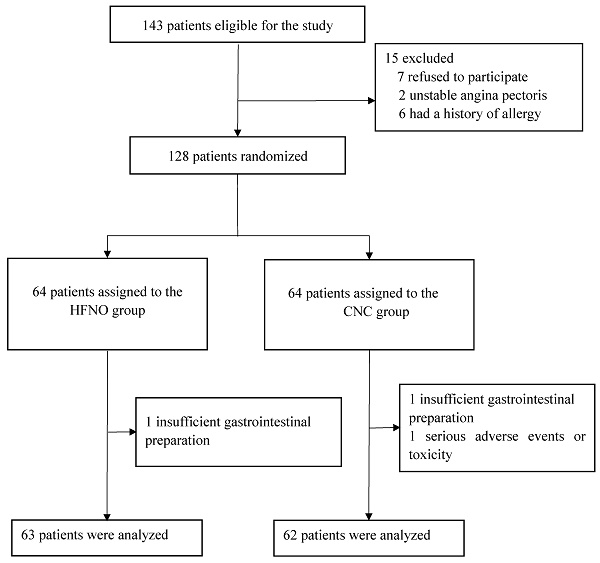
Methods: This study was a prospective, randomized, controlled trial conducted at a single center. We included elective patients aged 65 and above who were undergoing gastroscopy with sedation. In the intervention group (HFNO), we set the oxygen flow rate to 60 liters per minute with an oxygen fraction (FiO2) of 0.6, while in the control group (CNC), it was 6 liters per minute. The primary outcome was the occurrence of hypoxemia (defined as Spo2 < 90%).
Results: A total of 125 participants were enrolled (HFNO group: n = 63; CNC group: n = 62). The occurrence of hypoxemia was found to be significantly lower in the HFNO group compared to the CNC group (3.2% vs. 22.6%, p = 0.001). Additionally, a significantly shorter duration of low oxygen levels was observed in the HFNO group [0.0 seconds (0.0-13.0)] compared to the CNC group [0.0 seconds (0.0-124.0), p<0.001]. Moreover, a higher minimum Spo2 value was achieved in the HFNO group [99.0% (98.0-100.0) vs. 96.5% (91.0-99.0), p < 0.001], and a shorter recovery time was recorded [0.5 minutes (0.0-0.5) vs. 0.5 minutes (0.0-1.0), p = 0.016] in comparison to the CNC group. There were no differences in terms of comfort level [0 (0-4) vs. 0 (0-5), p = 0.268] between the two groups.
Conclusions: The HFNO system was determined to be a safe and highly effective method for oxygen delivery, leading to a reduction in the occurrence of hypoxemia in elderly patients undergoing gastroscopy with sedation. It is recommended that HFNO be considered as the standard approach for management in this population.
Keywords: desaturation, high-flow nasal oxygen, gastroscopy, sedation, elderly

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact