3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(12):1644-1661. doi:10.7150/ijms.86566 This issue Cite
Review
Preclinical models for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus - A practical approach for research
Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Center for Diabetes Metabolism Research, Cancer Center West China Hospital, West China School of Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
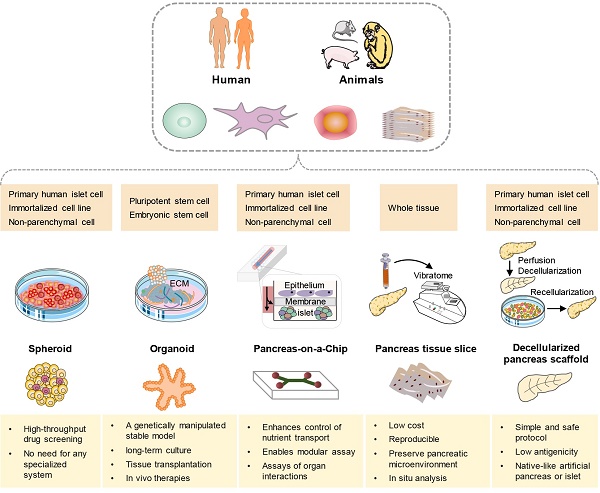
Numerous preclinical models have been developed to advance biomedical research in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). They are essential for improving our knowledge of T1DM development and progression, allowing researchers to identify potential therapeutic targets and evaluate the effectiveness of new medications. A deeper comprehension of these models themselves is critical not only to determine the optimal strategies for their utilization but also to fully unlock their potential applications in both basic and translational research. Here, we will comprehensively summarize and discuss the applications, advantages, and limitations of the commonly used animal models for human T1DM and also overview the up-to-date human tissue bioengineering models for the investigation of T1DM. By combining these models with a better understanding of the pathophysiology of T1DM, we can enhance our insights into disease initiation and development, ultimately leading to improved therapeutic responses and outcomes.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes mellitus, animal model, non-obese diabetic mice, streptozotocin, humanized model, bioengineering

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact