3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):985-992. doi:10.7150/ijms.84727 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of tuberculous tenosynovitis of the hand and wrist
1. Department of Geriatrics and Gerontology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
2. Department of Rheumatology, University Medical Center HCMC, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
3. Department of Orthopedics, University Medical Center HCMC, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
4. Department of Radiology, Pham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
*These authors contributed equally to this article as co-first authors.
Abstract
Objective: Vietnam is endemic with tuberculosis (TB), which is highly prevalent in the community. TB tenosynovitis of the wrist and hand is uncommon. Because of its insidious progression and atypical presentations, it is often difficult to diagnose, leading to treatment delays. This study investigates the characteristics of clinical and subclinical signs and treatment outcomes of patients with TB tenosynovitis in Vietnam.
Patients and Methods: This prospective longitudinal cross-sectional study included 25 TB tenosynovitis patients in the Rheumatology Clinic at University Medical Center Ho Chi Minh City. The diagnosis was made based on a tuberculous cyst in histopathological specimens. The data were collected through medical history, physical examination, and medical records, including demographics, signs, symptoms, condition duration, and related laboratory tests and imaging. The outcomes of all participants were assessed after 12 months of treatment.
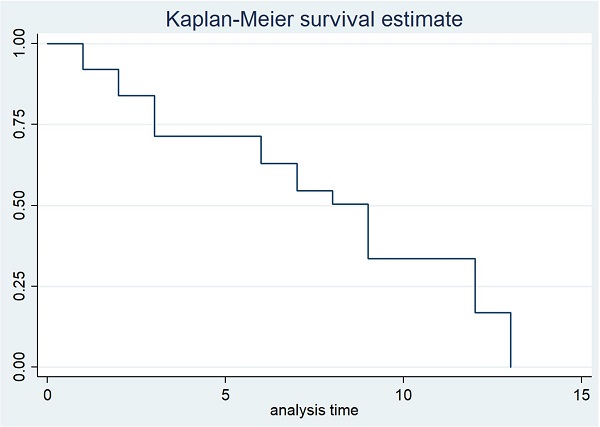
Results: The most common symptom of TB tenosynovitis was swelling of the hand and wrist, which was present in all patients. Its other symptoms included mild pain and numbness of the hand in 72% and 24% of patients, respectively. It can affect any site on the hand. Hand ultrasound findings included thickening of the synovial membrane (80%), peritendinous effusion (64%), and soft tissue swelling (88%). Most patients (18/22) had a good outcome after the treatment with anti-tubercular drugs.
Conclusions: TB tenosynovitis progression is often insidious. Its most common symptoms are swelling of the hand and mild pain. Ultrasound is a useful tool to support the diagnosis. A histological examination confirms the diagnosis. Most cases respond and have a good outcome after 9-12 months of anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Keywords: tuberculosis, tenosynovitis, wrist, hand

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact