3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):976-984. doi:10.7150/ijms.79619 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width as a Potential Valuable Survival Predictor in Hepatitis B Virus-related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Central Laboratory, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350001, China.
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Disease, Fuzong Clinical Medical College of Fujian Medical University (900TH Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force), Fuzhou, Fujian, 350025, China.
3. Follow-up Center of Union Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350001, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Objectives: Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is a widely used clinical parameter recently deployed in predicting various cancers. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of RDW in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
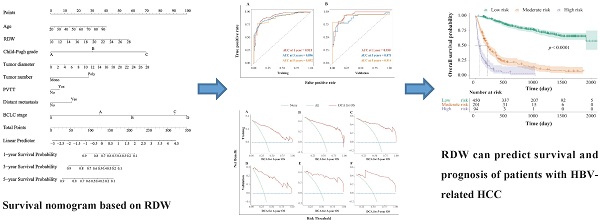
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of 745 patients with HBV-related HCC, 253 patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), and 256 healthy individuals to compare their hematological parameters and analyze their RDW levels. Potential risk factors for long-term all-cause mortality in patients with HBV-related HCC were predicted using Multivariate Cox regression. A nomogram was generated, and its performance was evaluated.
Results: The RDW of patients with HBV-related HCC was significantly higher than that of those with CHB and healthy controls. In the former, splenomegaly, liver cirrhosis, larger tumor diameter, multiple tumor number, portal vein tumor thrombus, and lymphatic or distant metastasis were significantly increased, and the later the Child-Pugh grade and Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage, the higher the RDW. Furthermore, multivariate Cox regression analysis identified RDW as an independent risk factor for predicting long-term all-cause mortality in patients with HBV-related HCC. Finally, we successfully generated a nomogram incorporating RDW and validated its predictive ability.
Conclusions: RDW is a potentially valuable hematological marker for predicting the survival and prognosis of patients with HBV-related HCC. The nomogram incorporating RDW can be used as an effective tool to plan the individualized treatment of such patients.
Keywords: Red blood cell distribution width, Prognosis, Nomogram, Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact