3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):933-942. doi:10.7150/ijms.82216 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LncRNA MIR155HG Overexpression Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Chemoresistance in Gastric Cancer Cells
1. Department of Etiology and Carcinogenesis, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Beijing Key Laboratory for Carcinogenesis and Cancer Prevention, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, P. R. China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, P. R. China.
Abstract
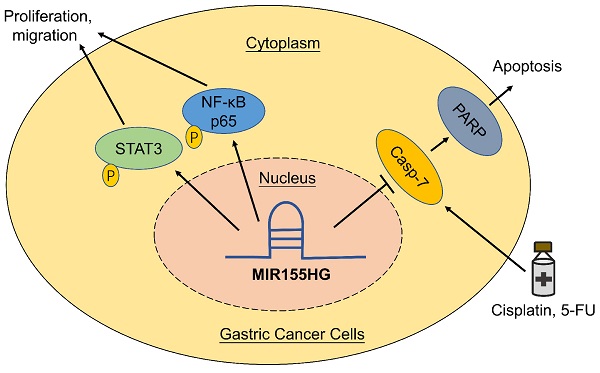
Long non-coding RNAs are thought to play a vital role in a variety of human malignancies. Studies have shown that MIR155 host gene (MIR155HG) acts as an oncogene in several cancers, but the function and its mechanism of MIR155HG in gastric cancer (GC) is still poorly understood. In this study, we determined the biological functions and underlying mechanisms of MIR155HG in GC cells. We found that expression levels of MIR155HG was increased markedly in GC patients' serum. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that MIR155HG modulated the malignant phenotype of GC cells, such as cell proliferation, colony forming ability, cell migration ability, and tumor growth in nude mice. Next, our results revealed that NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways could be involved in regulating the malignant behavior of GC cells. Our rescue experiments showed that inhibiting NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways attenuated the phenotypes caused by MIR155HG overexpression. Moreover, cytotoxicity and apoptosis assays revealed overexpression of MIR155HG reduced the apotosis of GC cells induced by cisplatin and 5-FU. Together, our studies suggested that MIR155HG overexpression promoted proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance of GC cells. These results might provide a lncRNA-based target for GC treatment in future.
Keywords: gastric cancer, MIR155HG, NF-κB, STAT3, chemoresistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact