3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(6):702-708. doi:10.7150/ijms.80837 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma and the subsequent open glaucoma development: a nationwide cohort study
1. Institute of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
2. Department of Ophthalmology, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan
3. Department of Optometry, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
4. Department of Post-Baccalaureate Medicine, College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan
5. Institute of Oral Sciences, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
6. Department of Otolaryngology, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
7. School of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
8. Nobel Eye Institute, Taipei, Taiwan
9. Department of Ophthalmology, Jen-Ai Hospital Dali Branch, Taichung, Taiwan;
10. Department of Medical Research, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
11. Department of Ophthalmology, Show Chwan Memorial Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan
Abstract
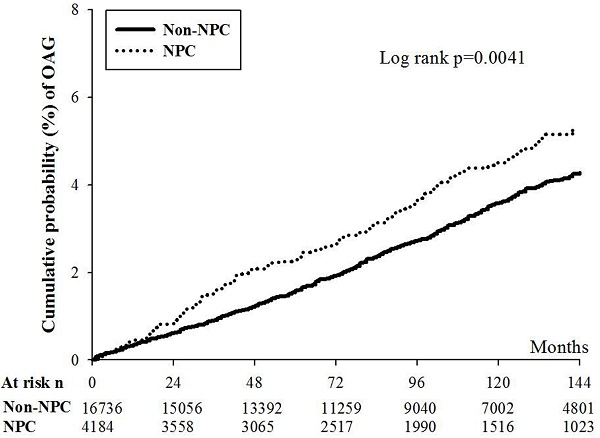
This study aimed to investigate the possible association between nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and following open angle glaucoma (OAG). A retrospective research applying the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) of Taiwan was conducted with a follow up period from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2016. There were 4184 and 16736 participants that selected and categorized into the NPC and non-NPC groups after exclusion. The major outcome of our study was the development of OAG according to diagnostic codes, exam and managements. The Cox proportional hazard regression was employed to estimate the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of OAG between the two groups. In this study, a numbers of 151 and 513 OAG episodes occurred in the NPC and non-NPC groups and the NPC population showed a significantly higher incidence of OAG compared to the non-NPC population in multivariable analysis (aHR: 1.293, 95% CI: 1.077-1.551, p = 0.0057). Besides, the cumulative probability of OAG was significantly higher in the NPC group than that in the non-NPC population (p = 0.0041). About other risk factor for OAG, age older than 40 years old, diabetes mellitus and persistent steroid usage were related to OAG occurrence (all p < 0.05). In conclusion, the NPC may be an independent risk factor of following OAG development.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, open angle glaucoma, age, epidemiology

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact